SpringBoot2 notes 黑马
# 01 - 开发环境
学习要求
- 熟悉 Spring 基础
- 熟悉 Maven 使用
环境要求
- Java8 及以上
- Maven 3.5 及以上:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/getting-started.html#getting-started-system-requirements
学习资料
- Spring Boot 官网:https://spring.io/projects/spring-boot
- Spring Boot 官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/
- Spring Boot 中文文档:http://felord.cn/_doc/_springboot/2.1.5.RELEASE/_book/
- 视频地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15b4y1a7yG?p=24&share_source=copy_web
- 源码地址:https://github.com/junwuyi/springboot-study
# 02 - 内容介绍
- 基础篇
Java基础语法
Spring与SpringMVC
知道Spring是用来管理bean,能够基于Restful实现页面请求交互功能
Mybatis与Mybatis-Plus
基于Mybatis和MybatisPlus能够开发出包含基础CRUD功能的标准Dao模块
数据库MySQL
能够读懂基础CRUD功能的SQL语句
服务器
知道服务器与web工程的关系,熟悉web服务器的基础配置
maven
知道maven的依赖关系,知道什么是依赖范围,依赖传递,排除依赖,可选依赖,继承
web技术(含vue,ElementUI)
知道vue如何发送ajax请求,如何获取响应数据,如何进行数据模型双向绑定
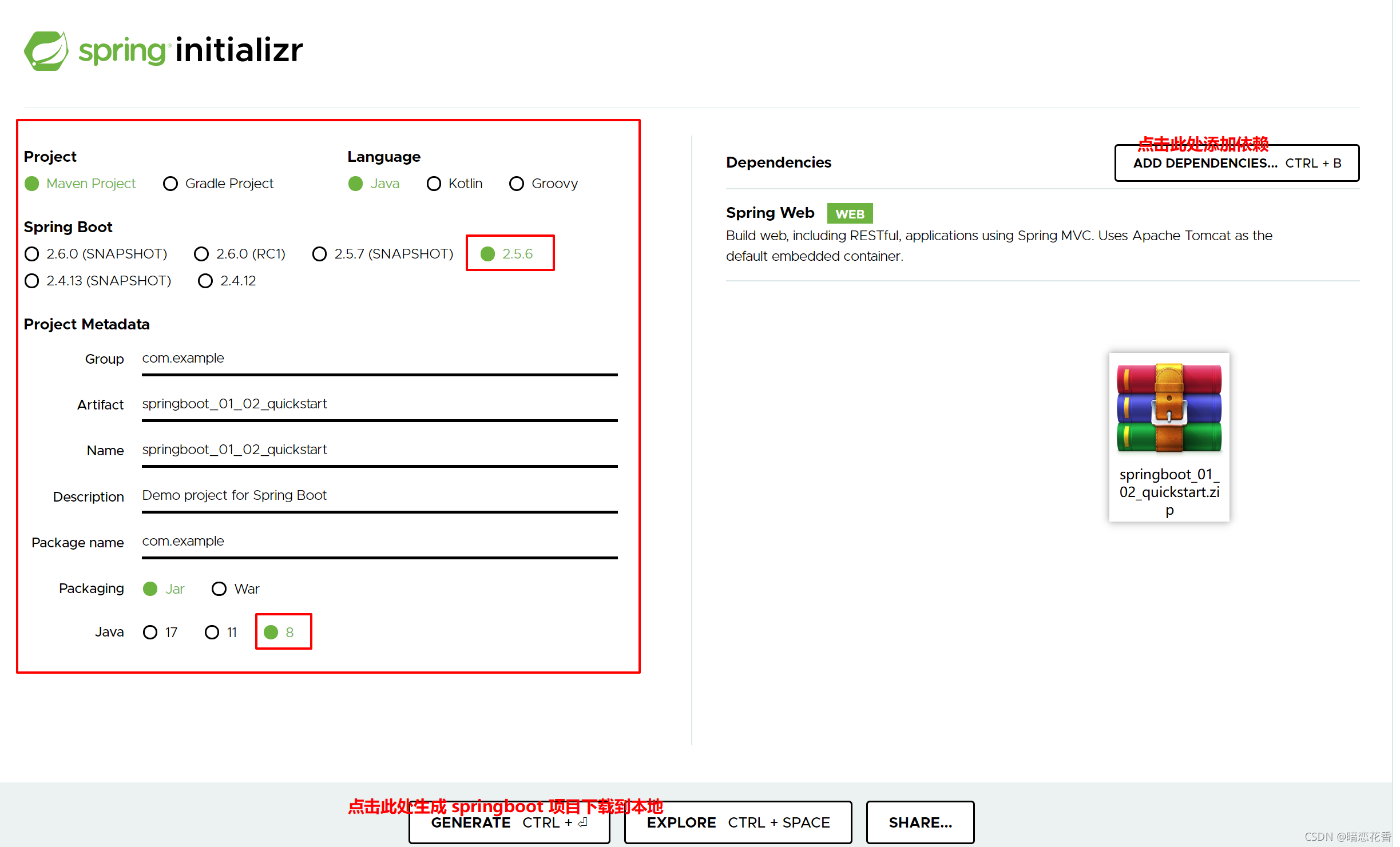
# 03-SpringBoot 入门案例(Idea 联网版)
- SpringBoot 是由 Pivotal 团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化 Spring 应用的初始搭建以及开发过程
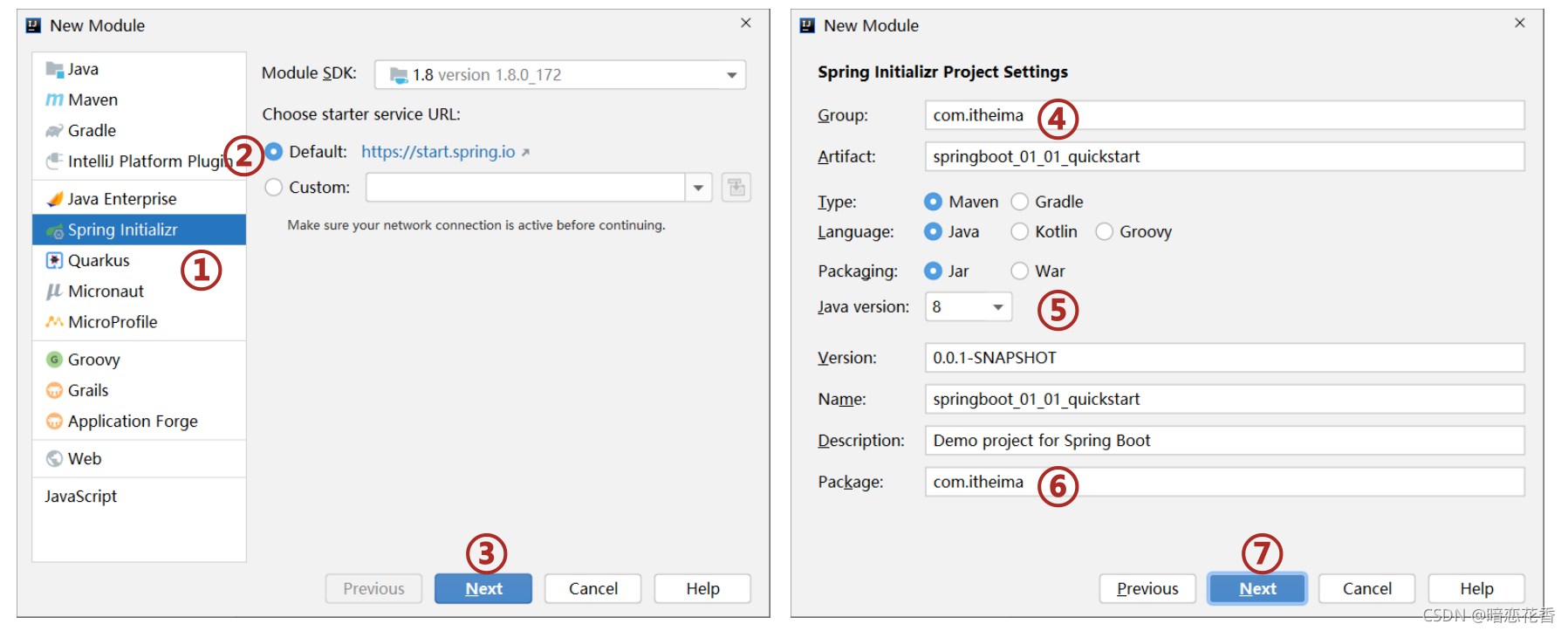
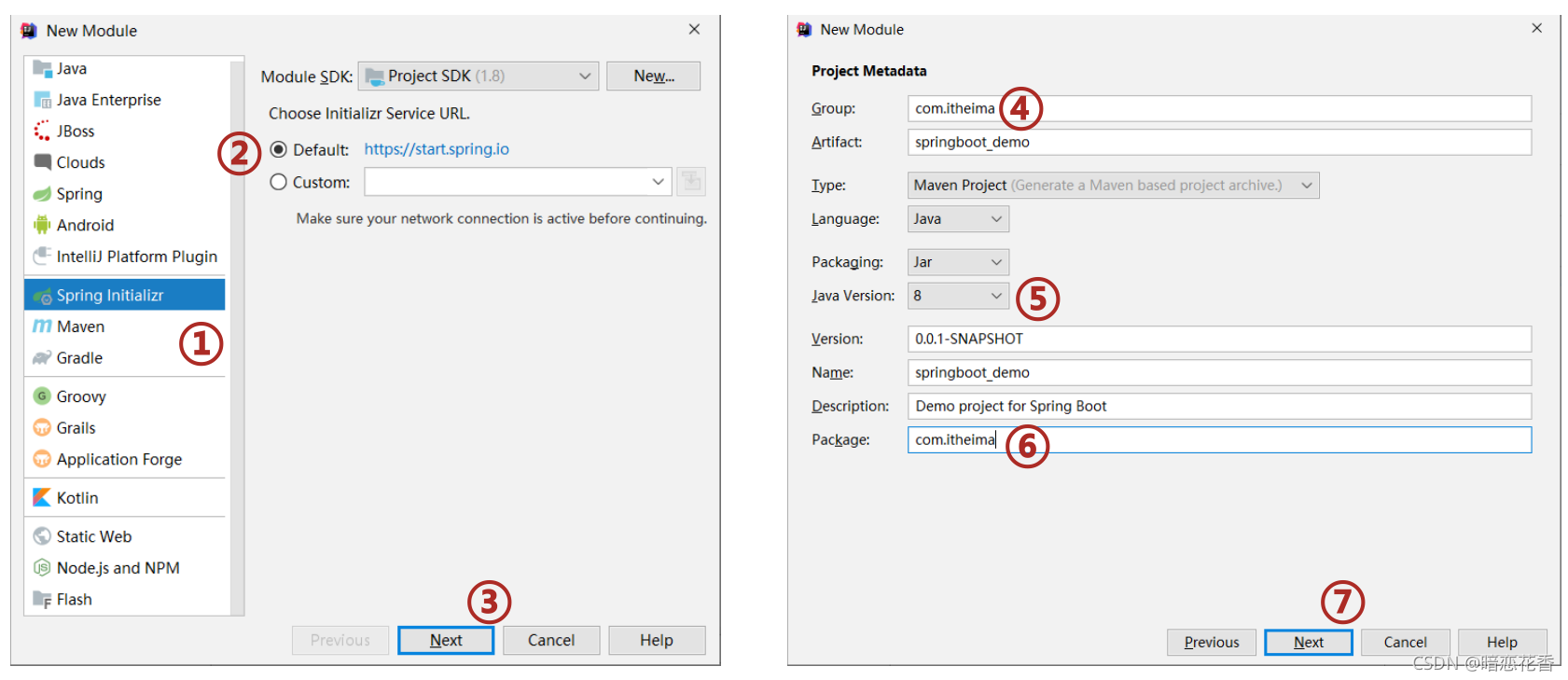
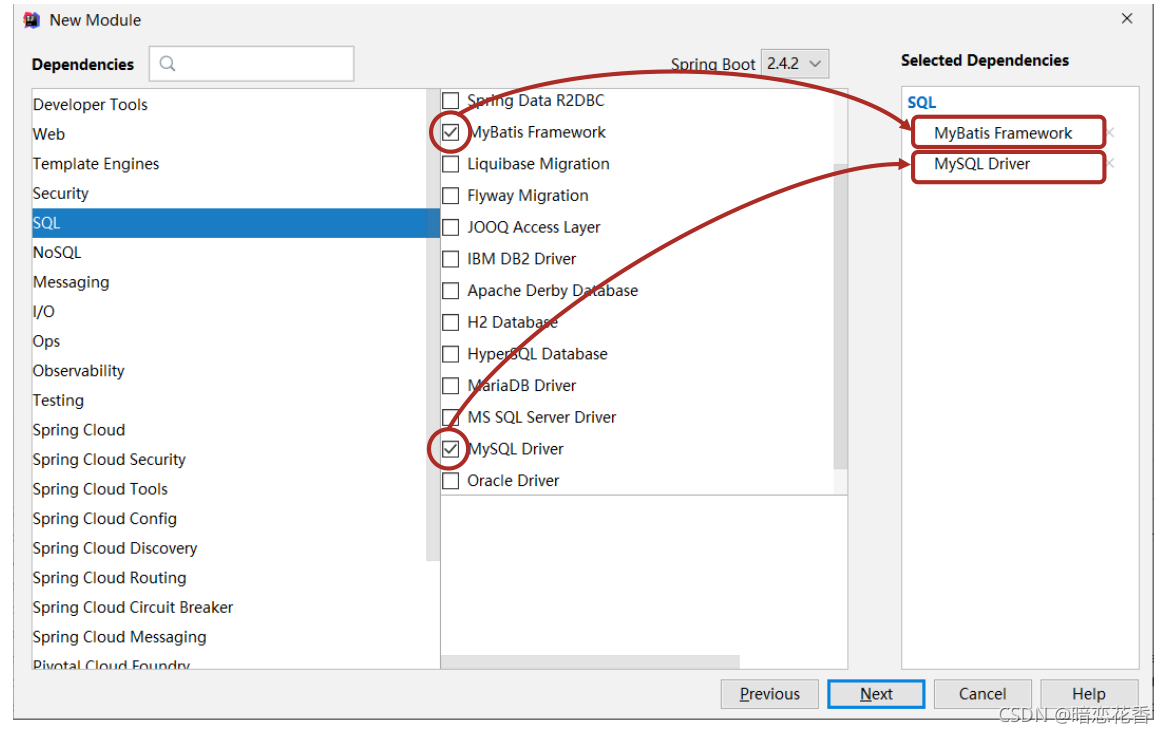
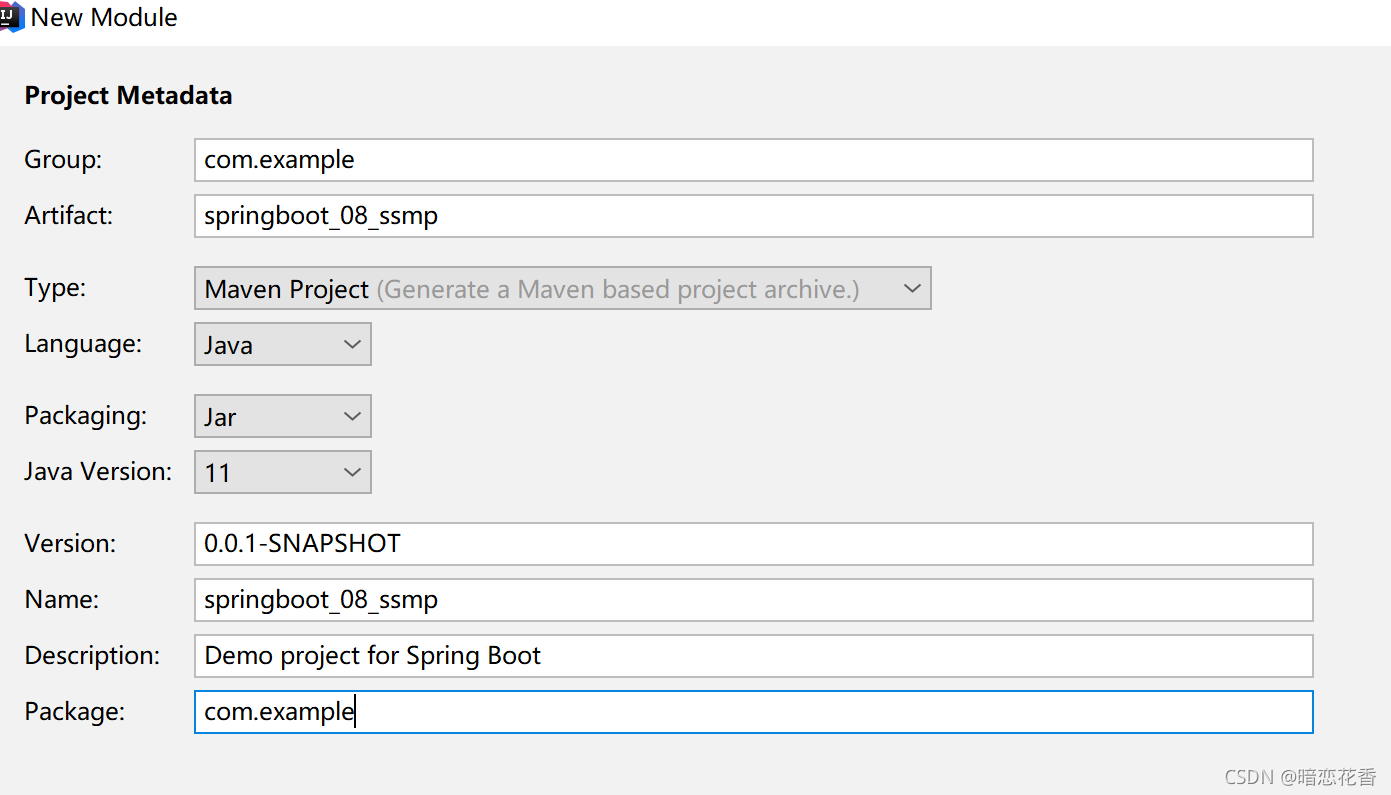
①:创建新模块,选择 Spring Initializr,并配置模块相关基础信息
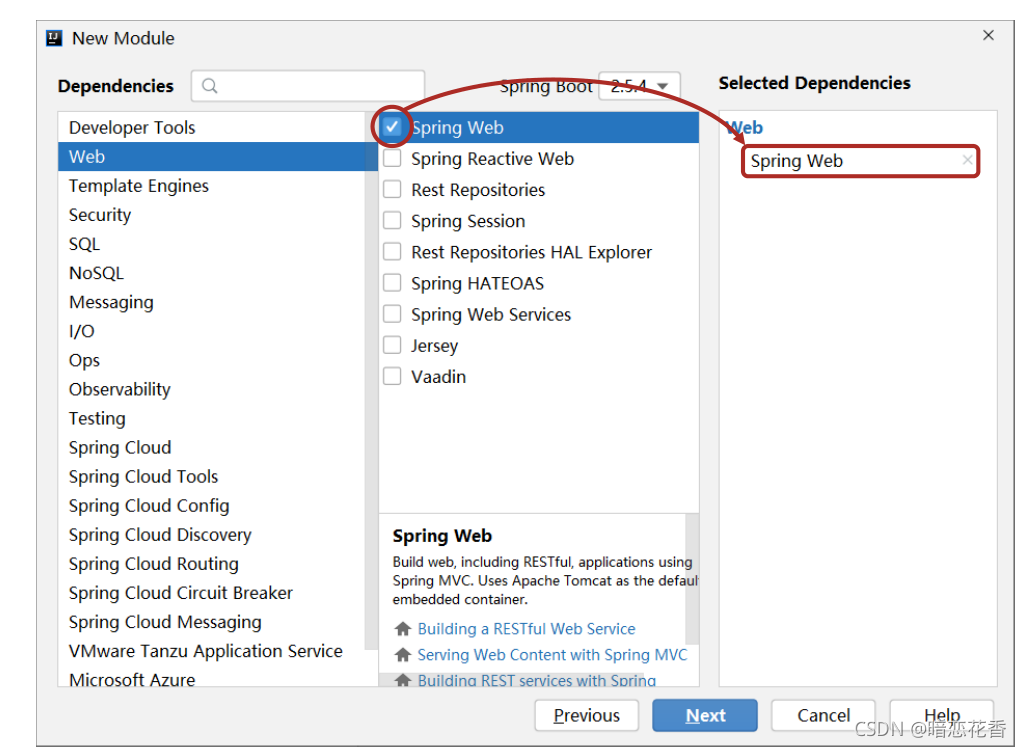
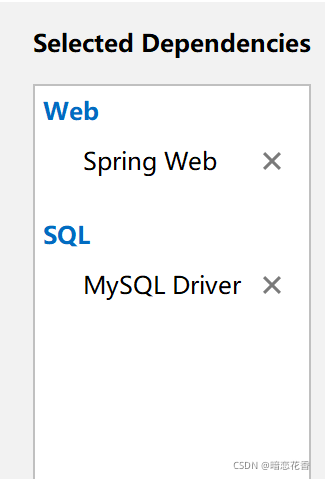
②:选择当前模块需要使用的技术集
③:开发控制器类
//Rest 模式
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping
public String getById() {
System.out.println("springboot is running...");
return "springboot is running...";
}
}
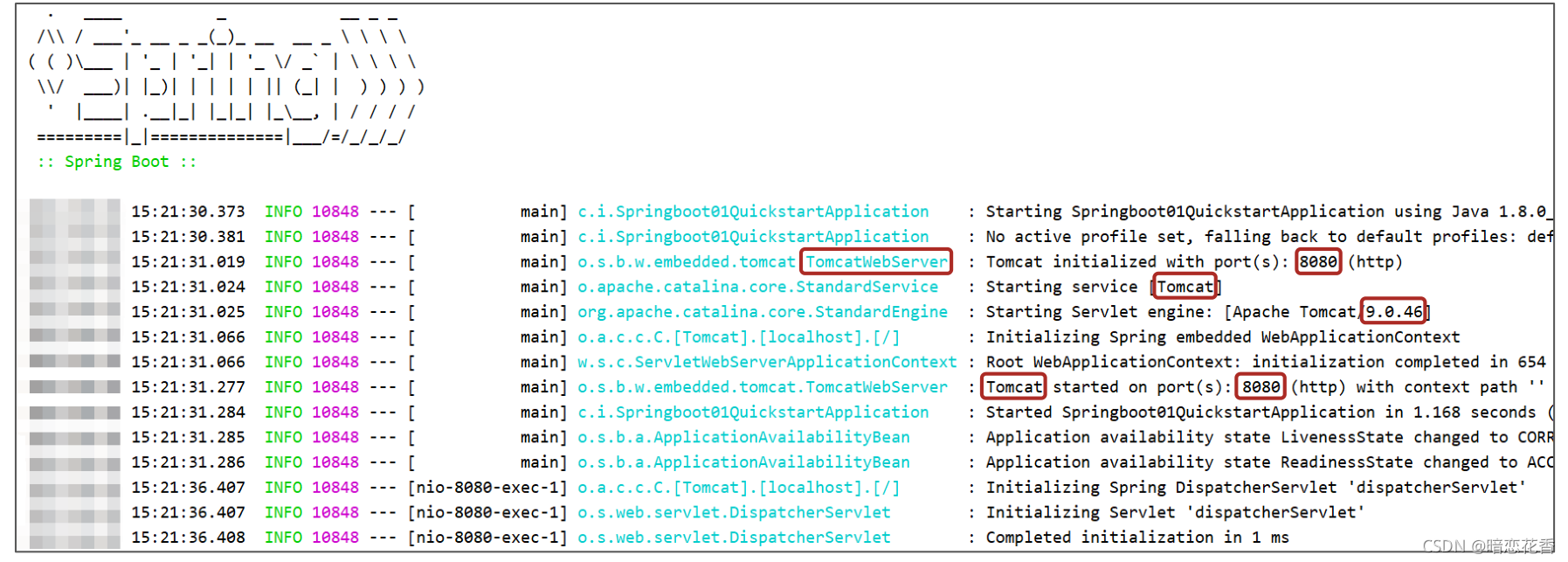
④:运行自动生成的 Application 类
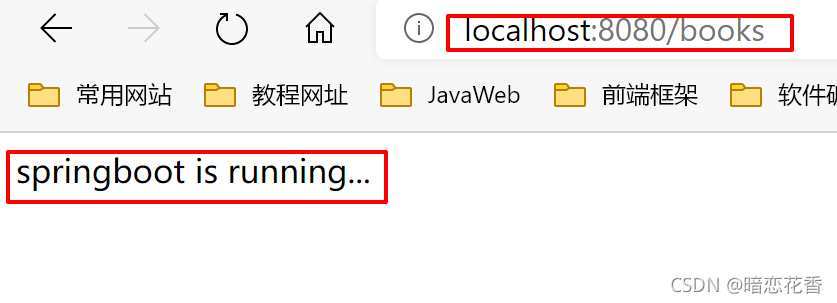
⑤:打开浏览器访问 url 地址为:http://localhost:8080/books
- 最简 SpringBoot 程序所包含的基础文件 (pom.xml 文件 和 Application 类)
- pom.xml 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-01-quickstart</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
- Application 类
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot0101QuickstartApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot0101QuickstartApplication.class, args);
}
}
-
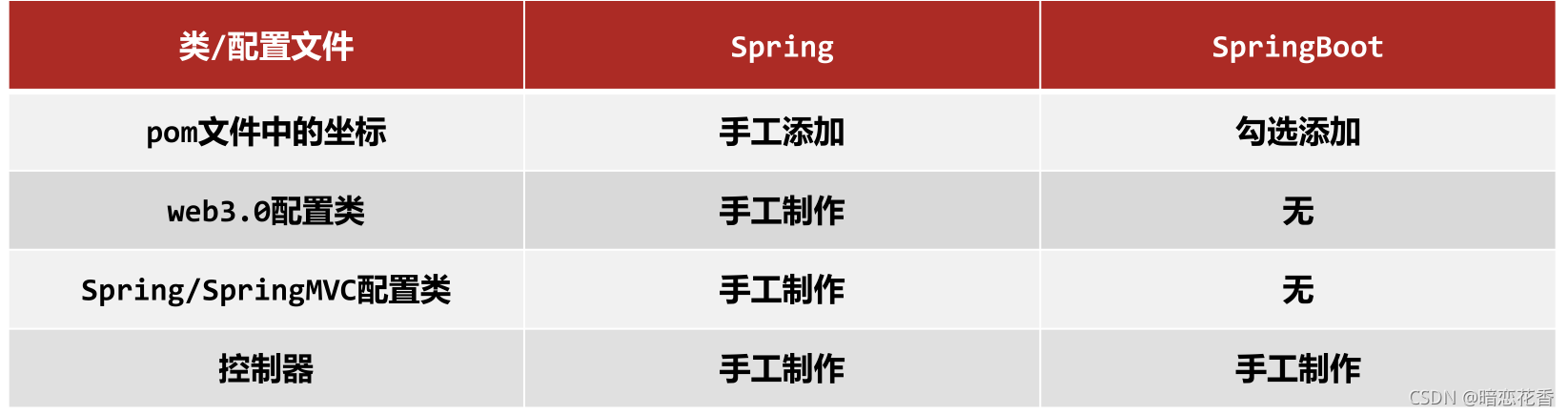
Spring 程序与 SpringBoot 程序对比
注意:基于 idea 开发 SpringBoot 程序需要确保联网且能够加载到程序框架结构
小结:
- 开发 SpringBoot 程序可以根据向导进行联网快速制作
- SpringBoot 程序需要基于 JDK8 进行制作
- SpringBoot 程序中需要使用何种功能通过勾选选择技术
- 运行 SpringBoot 程序通过运行 Application 程序入口进行
# 04-SpringBoot 入门案例(官网创建版)
- 基于 SpringBoot 官网创建项目,地址:https://start.spring.io/
小结:
- 打开 SpringBoot 官网,选择 Quickstart Your Project
- 创建工程,并保存项目
- 解压项目,通过 IDE 导入项目
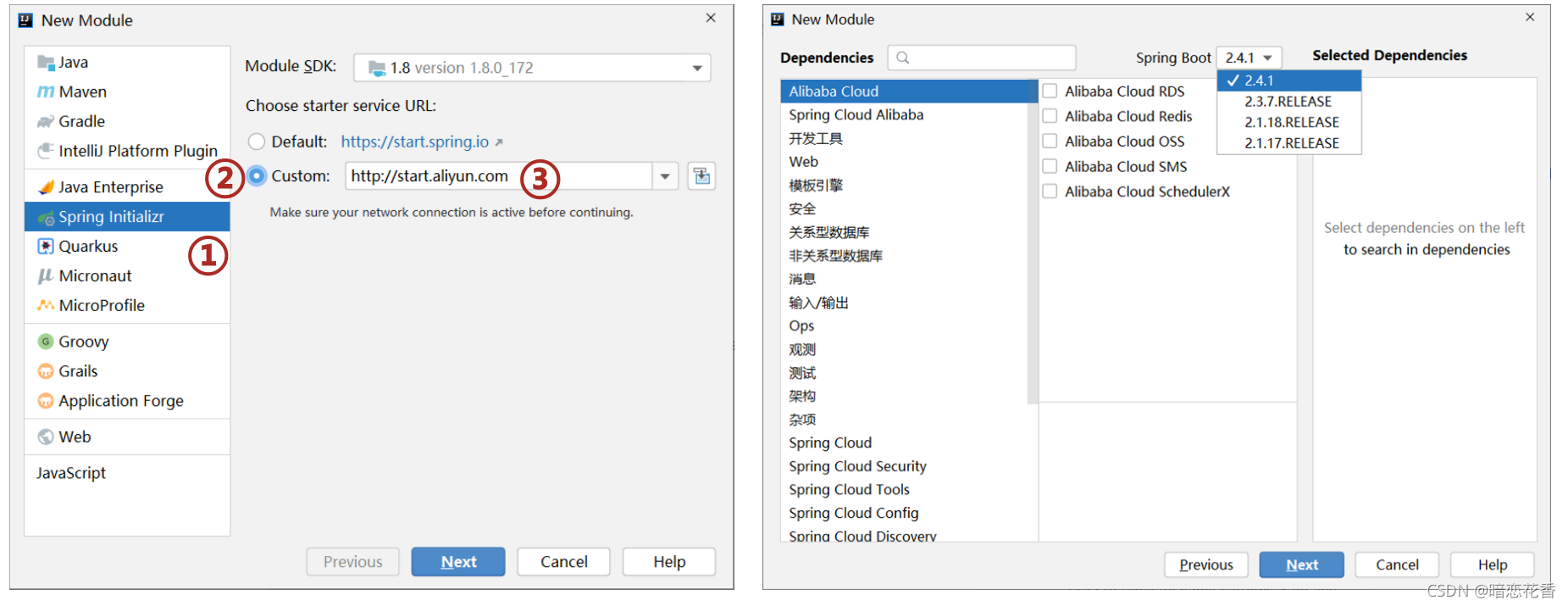
# 05-SpringBoot 入门案例(阿里云版)
- 基于阿里云创建项目,地址:https://start.aliyun.com
注意事项:
- 阿里云提供的坐标版本较低,如果需要使用高版本,进入工程后手工切换 SpringBoot 版本
- 阿里云提供的工程模板与 Spring 官网提供的工程模板略有不同
小结:
- 选择 start 来源为自定义 URL
- 输入阿里云 start 地址
- 创建项目
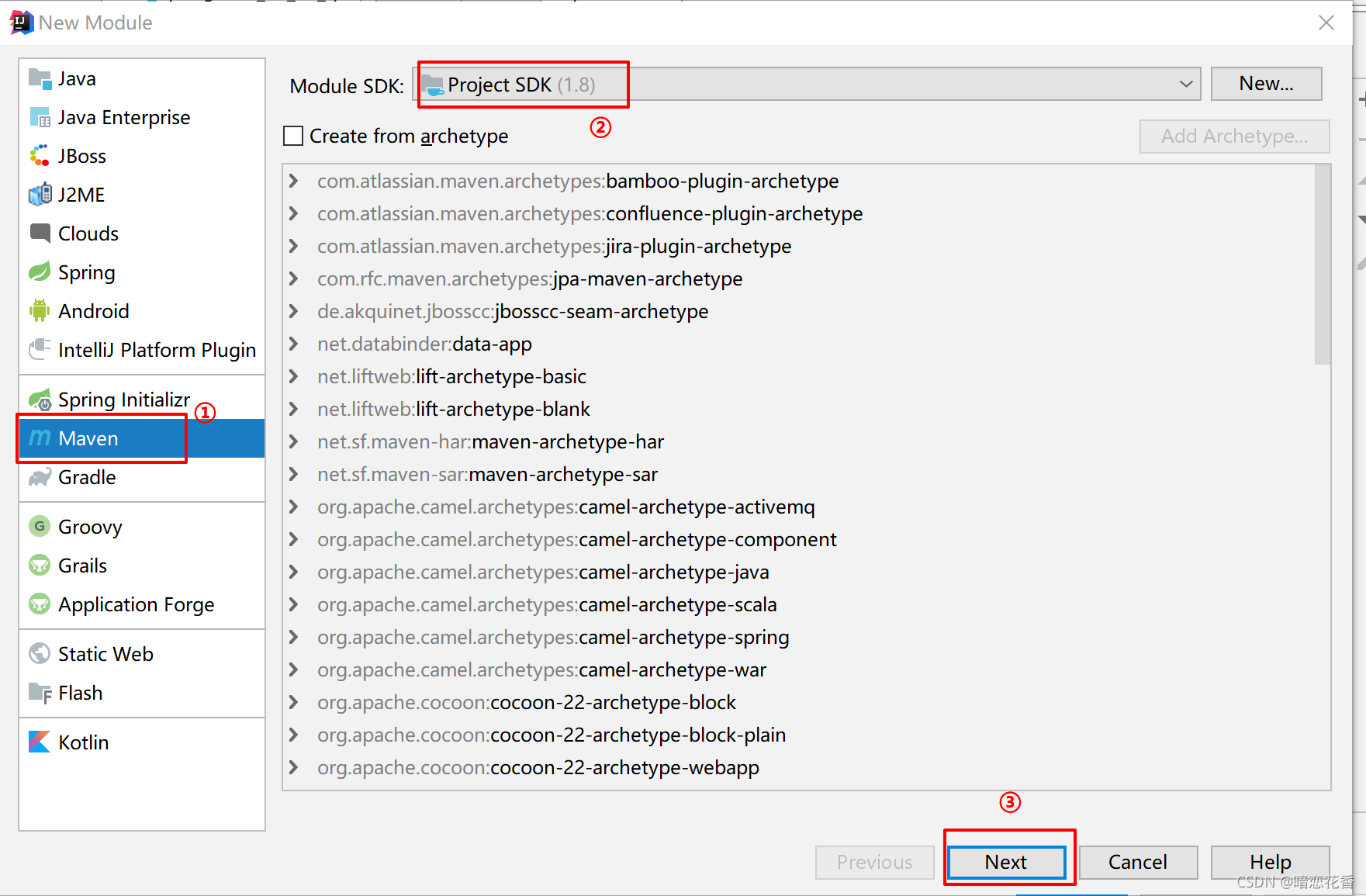
# 06-SpringBoot 入门案例(手工制作版)
- 手工创建项目(手工导入坐标)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot_01_04_quickstart</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
- 手工创建项目(手工制作引导类)
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
小结:
- 创建普通 Maven 工程
- 继承 spring-boot-starter-parent
- 添加依赖 spring-boot-starter-web
- 制作引导类 Application
总结:
- 创建 SpringBoot 工程的四种方式
基于 Idea 创建 SpringBoot 工程
基于官网创建 SpringBoot 工程
基于阿里云创建 SpringBoot 工程
手工创建 Maven 工程修改为 SpringBoot 工程
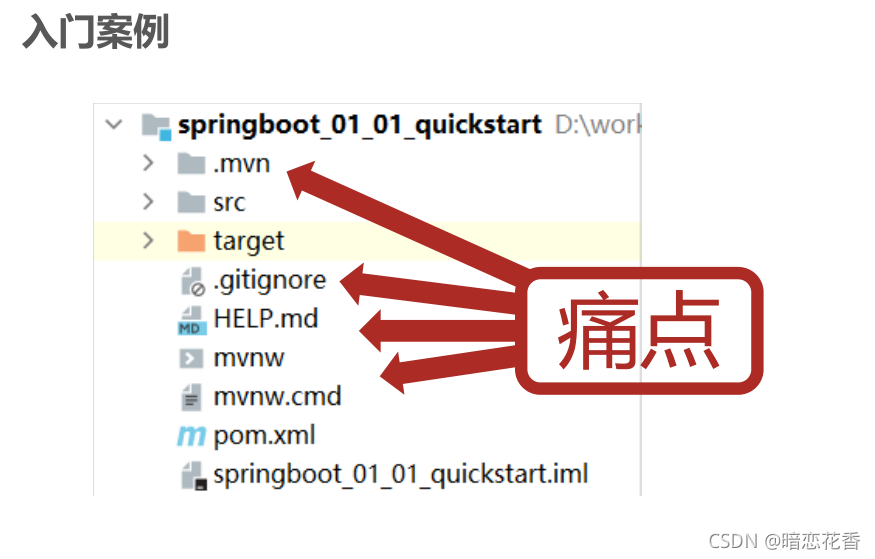
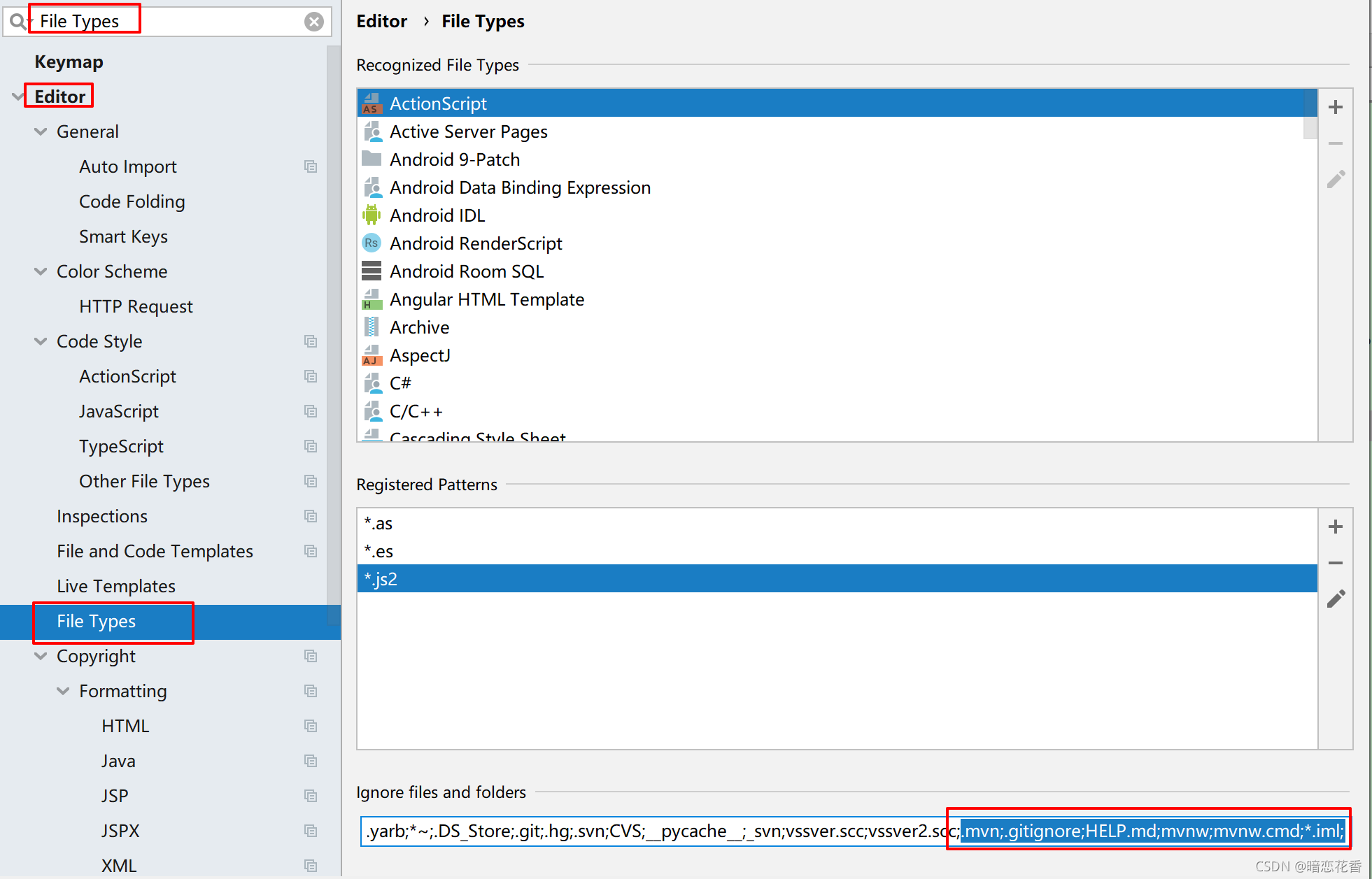
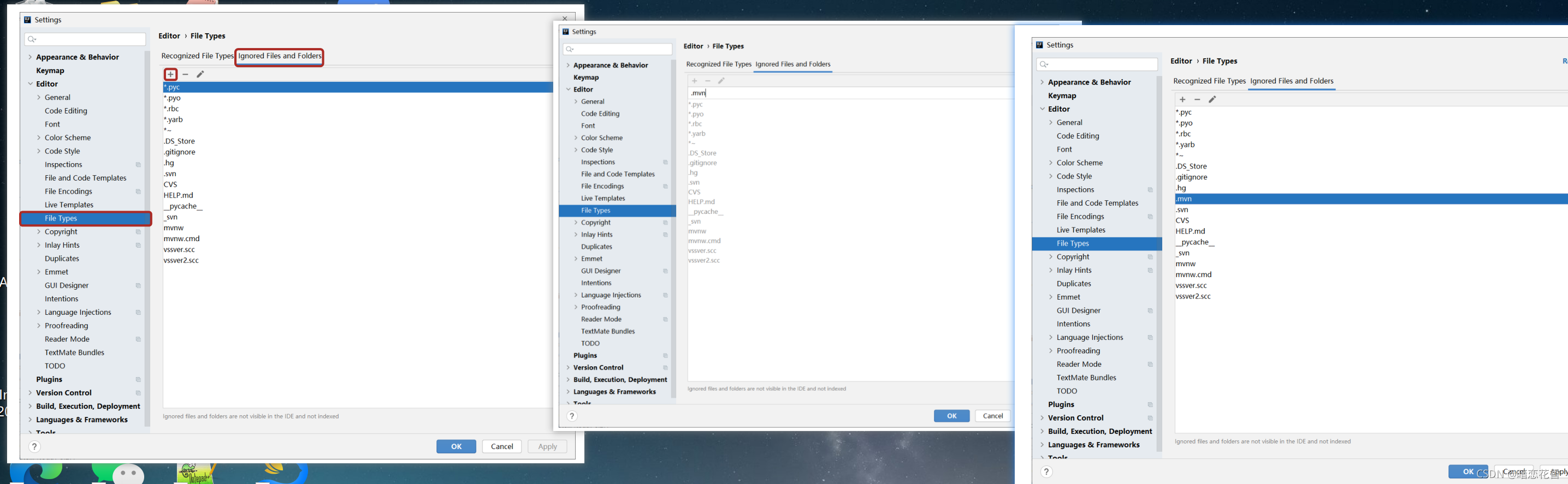
# 07 - 教你一招:隐藏文件或文件夹
- .mvn;.gitignore;HELP.md;mvnw;mvnw.cmd;*.iml;
2018 版的做法:
较新版本的做法 :
小结:
- Idea 中隐藏指定文件或指定类型文件
Setting → File Types → Ignored Files and Folders
输入要隐藏的文件名,支持 * 号通配符
回车确认添加
# 08 - 入门案例解析:parent
- parent
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-01-quickstart</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
按住 Ctrl 点击 pom.xml 中的 spring-boot-starter-parent,跳转到了 spring-boot-starter-parent 的 pom.xml,xml 配置如下(只摘抄了部分重点配置):
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</parent>
按住 Ctrl 点击 pom.xml 中的 spring-boot-starter-dependencies,跳转到了 spring-boot-starter-dependencies 的 pom.xml,xml 配置如下(只摘抄了部分重点配置):
`<properties>
<activemq.version>5.15.3</activemq.version>
<antlr2.version>2.7.7</antlr2.version>
<appengine-sdk.version>1.9.63</appengine-sdk.version>
<artemis.version>2.4.0</artemis.version>
<aspectj.version>1.8.13</aspectj.version>
<assertj.version>3.9.1</assertj.version>
<atomikos.version>4.0.6</atomikos.version>
<bitronix.version>2.1.4</bitronix.version>
<build-helper-maven-plugin.version>3.0.0</build-helper-maven-plugin.version>
<byte-buddy.version>1.7.11</byte-buddy.version>
... ... ...
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
... ... ...
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId>
<artifactId>kotlin-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${kotlin.version}</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jooq</groupId>
<artifactId>jooq-codegen-maven</artifactId>
<version>${jooq.version}</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</plugin>
... ... ...
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
* 40
* 41
* 42
* 43
* 44
* 45
* 46
* 47
* 48
* 49
* 50
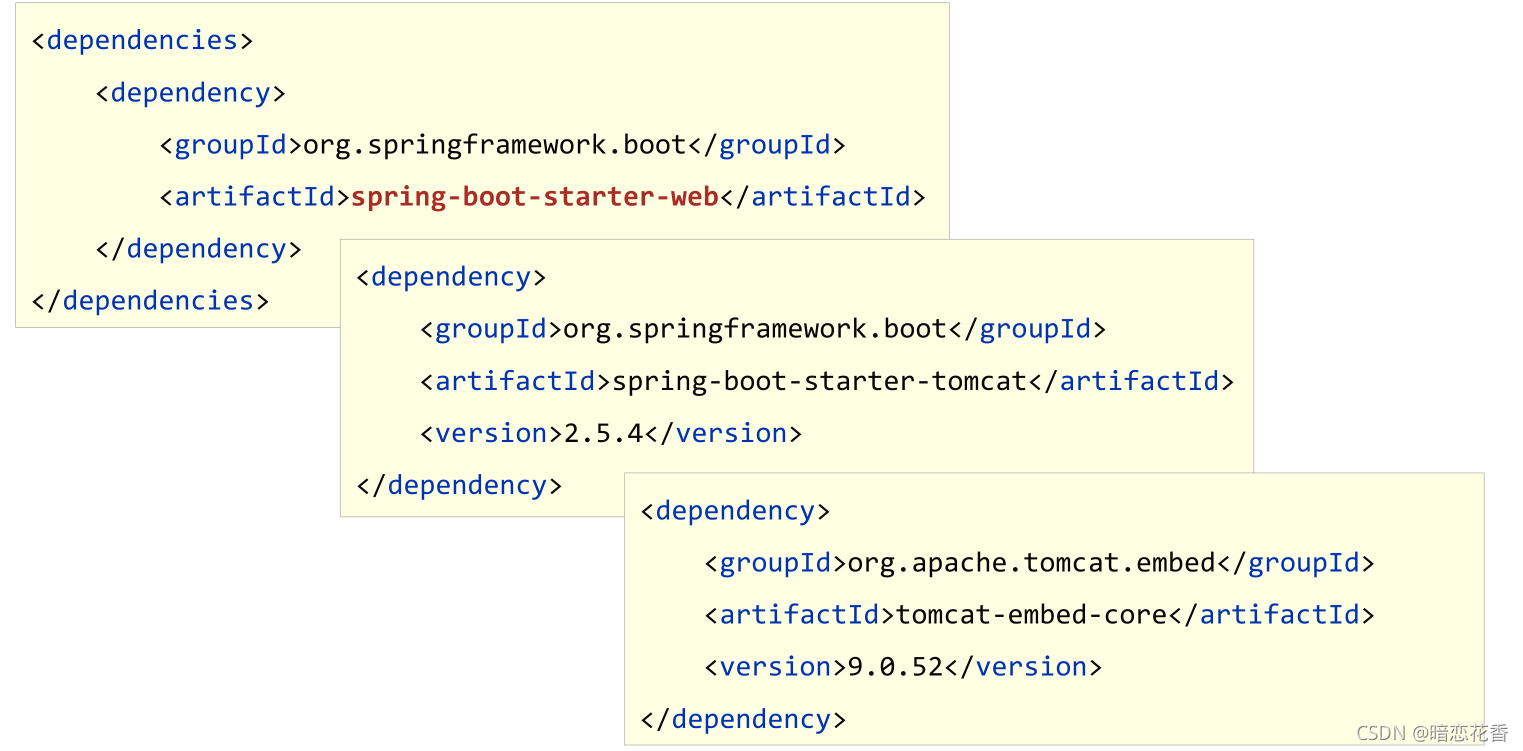
从上面的 spring-boot-starter-dependencies 的 pom.xml 中我们可以发现,一部分坐标的版本、依赖管理、插件管理已经定义好,所以我们的 SpringBoot 工程继承 spring-boot-starter-parent 后已经具备版本锁定等配置了。所以起步依赖的作用就是进行依赖的传递。
小结:
- 开发 SpringBoot 程序要继承 spring-boot-starter-parent
- spring-boot-starter-parent 中定义了若干个依赖管理
- 继承 parent 模块可以避免多个依赖使用相同技术时出现依赖版本冲突
- 继承 parent 的形式也可以采用引入依赖的形式实现效果
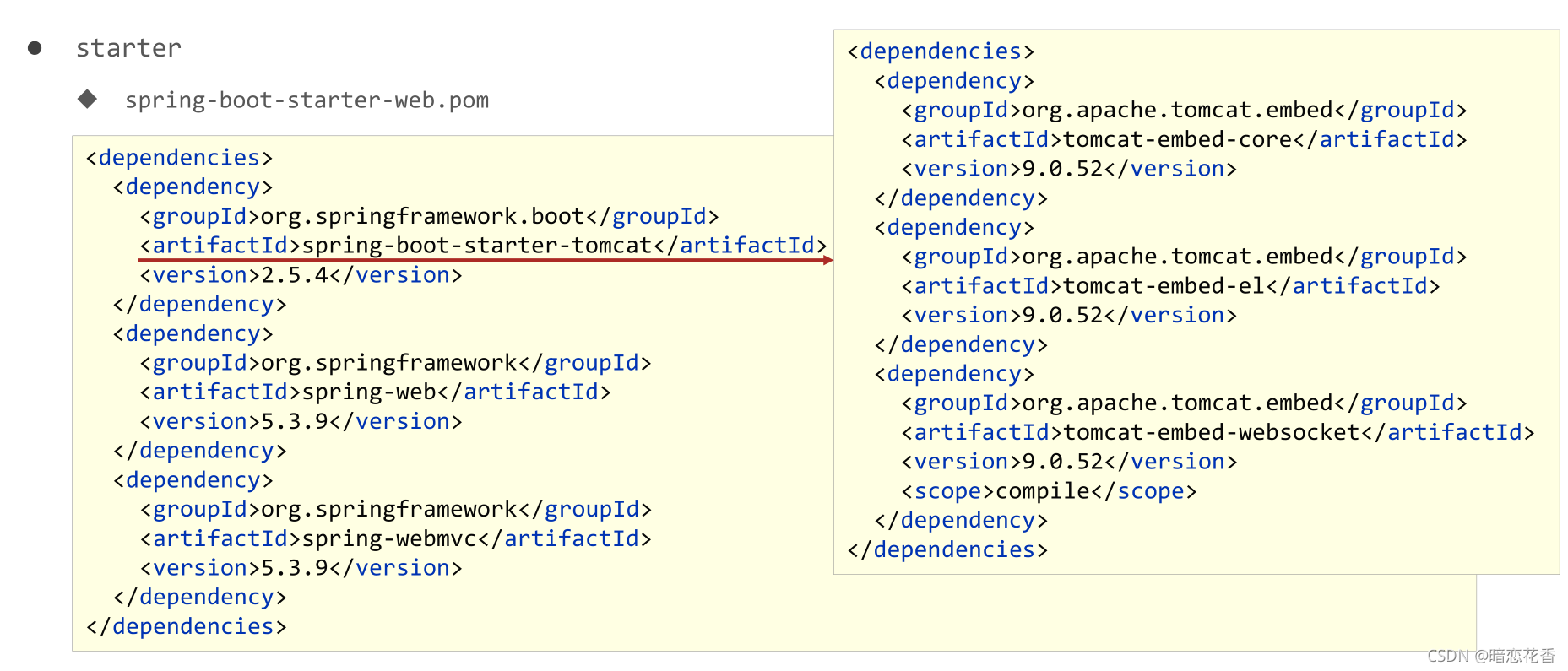
# 09 - 入门案例解析:starter
- spring-boot-starter-web.pom
按住 Ctrl 点击 pom.xml 中的 spring-boot-starter-web,跳转到了 spring-boot-starter-web 的 pom.xml,xml 配置如下(只摘抄了部分重点配置):
`<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starters</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<name>Spring Boot Web Starter</name>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.0.9.Final</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
* 40
* 41
* 42
* 43
* 44
* 45
* 46
* 47
* 48
* 49
* 50
* 51
* 52
* 53
从上面的 spring-boot-starter-web 的 pom.xml 中我们可以发现,spring-boot-starter-web 就是将 web 开发要使用的 spring-web、spring-webmvc 等坐标进行了 “打包”,这样我们的工程只要引入 spring-boot-starter-web 起步依赖的坐标就可以进行 web 开发了,同样体现了依赖传递的作用。
- starter
SpringBoot 中常见项目名称,定义了当前项目使用的所有依赖坐标,以达到减少依赖配置的目的 - parent
所有 SpringBoot 项目要继承的项目,定义了若干个坐标版本号(依赖管理,而非依赖),以达到减少依赖冲突的目的
spring-boot-starter-parent 各版本间存在着诸多坐标版本不同 - 实际开发
使用任意坐标时,仅书写 GAV (groupId, artifactId, version) 中的 G 和 A,V 由 SpringBoot 提供,除非 SpringBoot 未提供对应版本 V
如发生坐标错误,再指定 Version(要小心版本冲突)
小结:
- 开发 SpringBoot 程序需要导入坐标时通常导入对应的 starter
- 每个不同的 starter 根据功能不同,通常包含多个依赖坐标
- 使用 starter 可以实现快速配置的效果,达到简化配置的目的
# 10 - 入门案例解析:引导类
- 启动方式
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot0101QuickstartApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Springboot0101QuickstartApplication.class, args);
//获取bean对象
BookController bean = ctx.getBean(BookController.class);
System.out.println("bean======>" + bean);
}
}
- SpringBoot 的引导类是 Boot 工程的执行入口,运行 main 方法就可以启动项目
- SpringBoot 工程运行后初始化 Spring 容器,扫描引导类所在包加载 bean
小结:
- SpringBoot 工程提供引导类用来启动程序
- SpringBoot 工程启动后创建并初始化 Spring 容器
# 11 - 入门案例:辅助功能
-
辅助功能 内嵌 tomcat
-
使用 maven 依赖管理变更起步依赖项
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!--web 起步依赖环境中,排除 Tomcat 起步依赖 -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加 Jetty 起步依赖,版本由 SpringBoot 的 starter 控制 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- Jetty 比 Tomcat 更轻量级,可扩展性更强(相较于 Tomcat),谷歌应用引擎(GAE)已经全面切换为 Jetty
- 内置服务器
tomcat (默认) apache 出品,粉丝多,应用面广,负载了若干较重的组件
jetty 更轻量级,负载性能远不及 tomcat
undertow undertow,负载性能勉强跑赢 tomcat
小结:
- 内嵌 Tomcat 服务器是 SpringBoot 辅助功能之一
- 内嵌 Tomcat 工作原理是将 Tomcat 服务器作为对象运行,并将该对象交给 Spring 容器管理
- 变更内嵌服务器思想是去除现有服务器,添加全新的服务器
# 总结:
- 入门案例(4 种方式)
- SpringBoot 概述
parent
starter
引导类
辅助功能(内嵌 tomcat)
# [补] 知识加油站 - 01-REST 风格简介
-
什么是 rest :
-
REST(Representational State Transfer)表现形式状态转换
-
传统风格资源描述形式
http://localhost/user/getById?id=1 (得到 id 为 1 的用户)
http://localhost/user/saveUser (保存用户) -
REST 风格描述形式
http://localhost/user/1 (得到 id 为 1 的用户)
http://localhost/user (保存用户)
-
-
优点:
- 隐藏资源的访问行为, 无法通过地址得知对资源是何种操作
- 书写简化
-
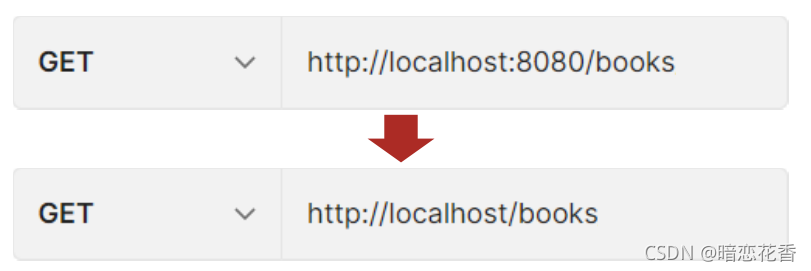
按照 REST 风格访问资源时使用行为动作区分对资源进行了何种操作
GET 用来获取资源,POST 用来新建资源,PUT 用来更新资源,DELETE 用来删除资源
- http://localhost/users 查询全部用户信息 GET (查询)
- http://localhost/users/1 查询指定用户信息 GET (查询)
- http://localhost/users 添加用户信息 POST (新增 / 保存)
- http://localhost/users 修改用户信息 PUT (修改 / 更新)
- http://localhost/users/1 删除用户信息 DELETE (删除)
注意:
上述行为是约定方式,约定不是规范,可以打破,所以称 REST 风格,而不是 REST 规范
描述模块的名称通常使用复数,也就是加 s 的格式描述,表示此类资源,而非单个资源,例如: users、 books、 accounts… -
根据 REST 风格对资源进行访问称为 RESTful
-
小结:
- REST
- 动作 4 个
- RESTful
# [补] 知识加油站 - 02-RESTful 入门案例
步骤:
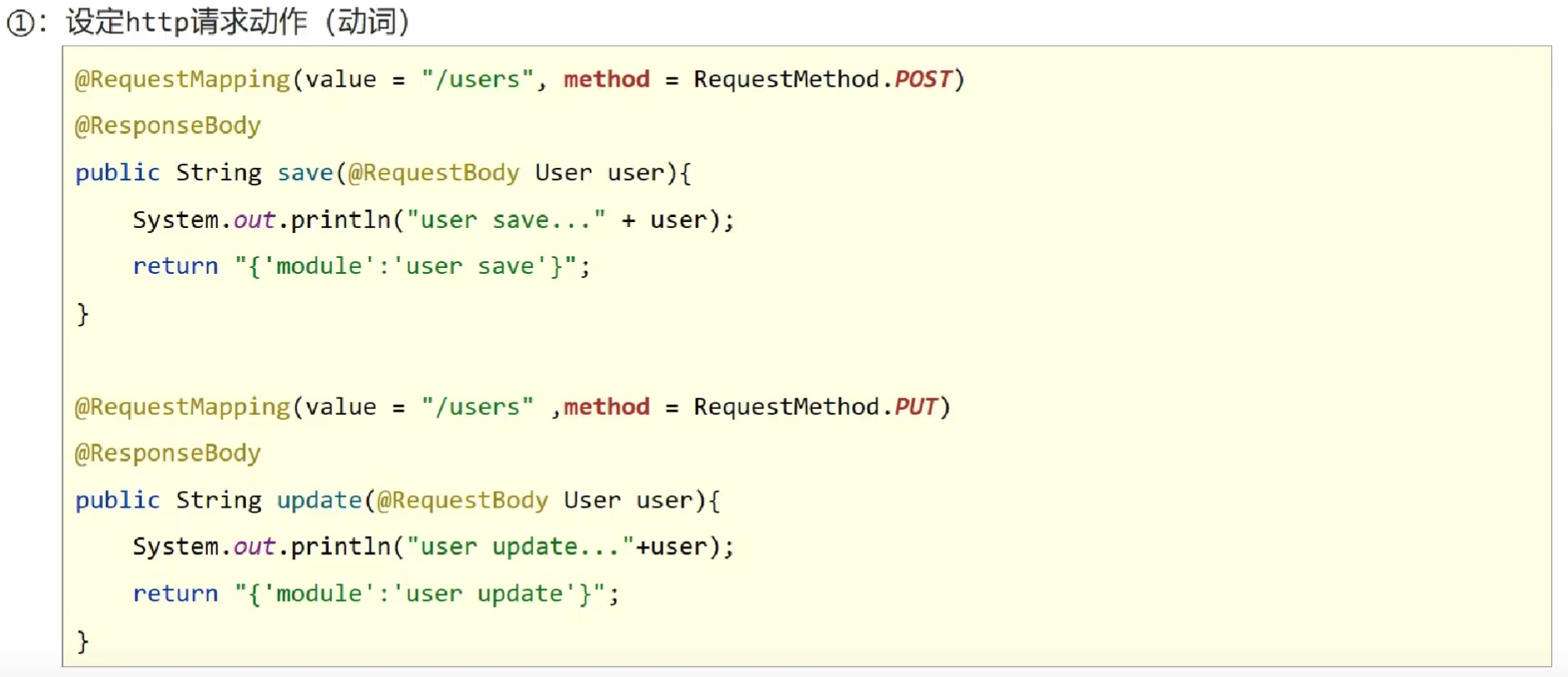
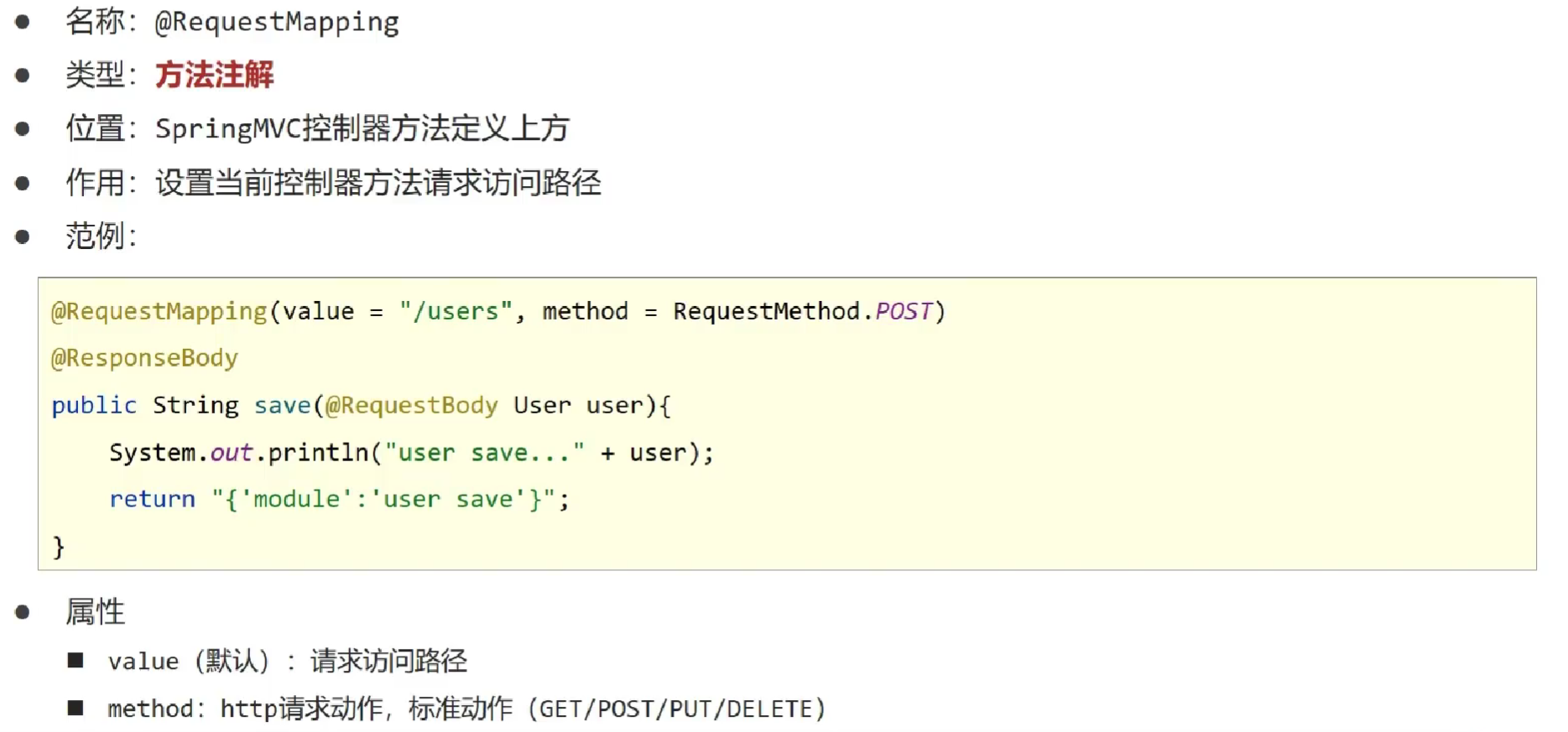
①: 设定 http 请求动作 (动词)
使用 @RequestMapping 注解的 method 属性声明请求的方式
使用 @RequestBody 注解 获取请求体内容。直接使用得到是 key=value&key=value… 结构的数据。get 请求方式不适用。
使用 @ResponseBody 注解实现将 controller 方法返回对象转换为 json 响应给客户端。
@RequestMapping(value="/users",method=RequestMethod.POST)
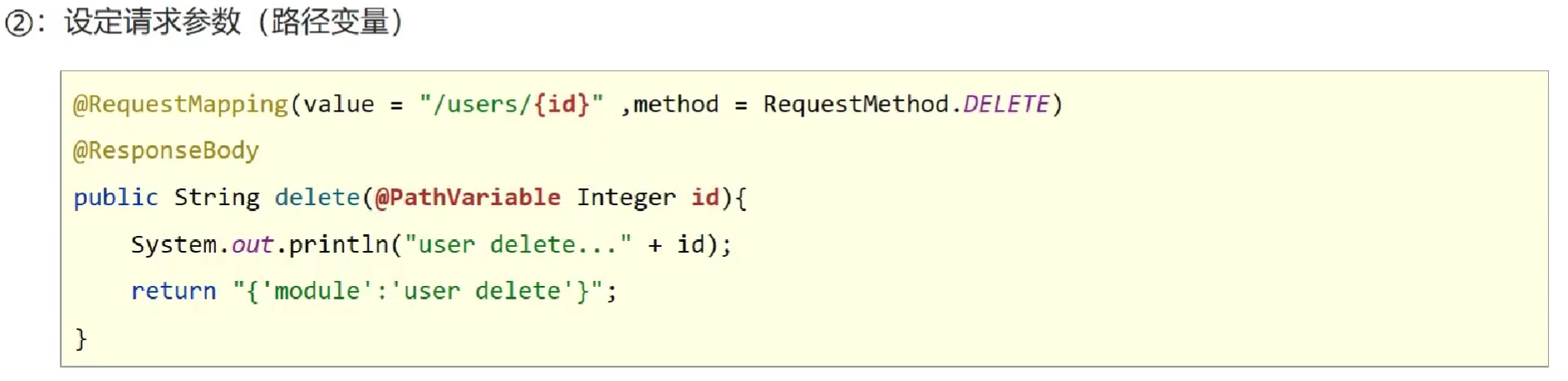
②: 设定请求参数 (路径变量)
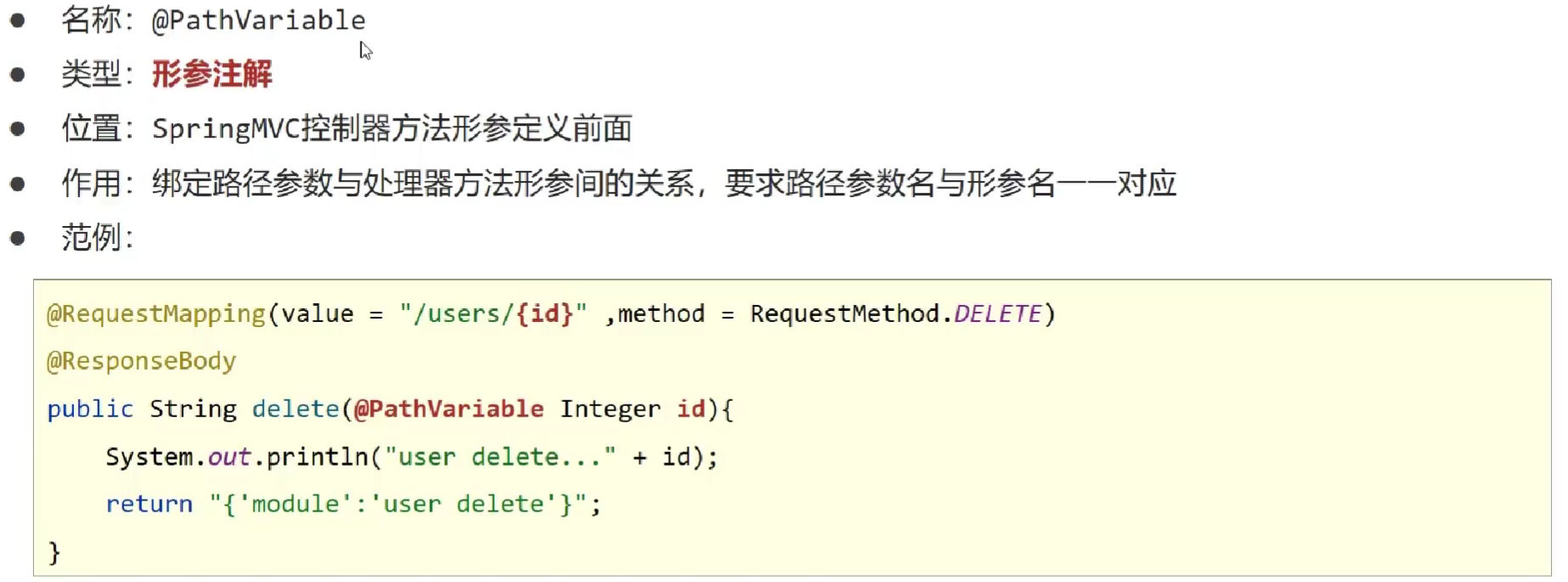
使用 @PathVariable 用于绑定 url 中的占位符。例如:请求 url 中 /delete/ {id} ,这个 {id} 就是 url 占位符。
- @RequestMapping
- @PathVariable
- @RequestBody @RequestParam @PathVariable
# [补] 知识加油站 - 03-RESTful 快速开发
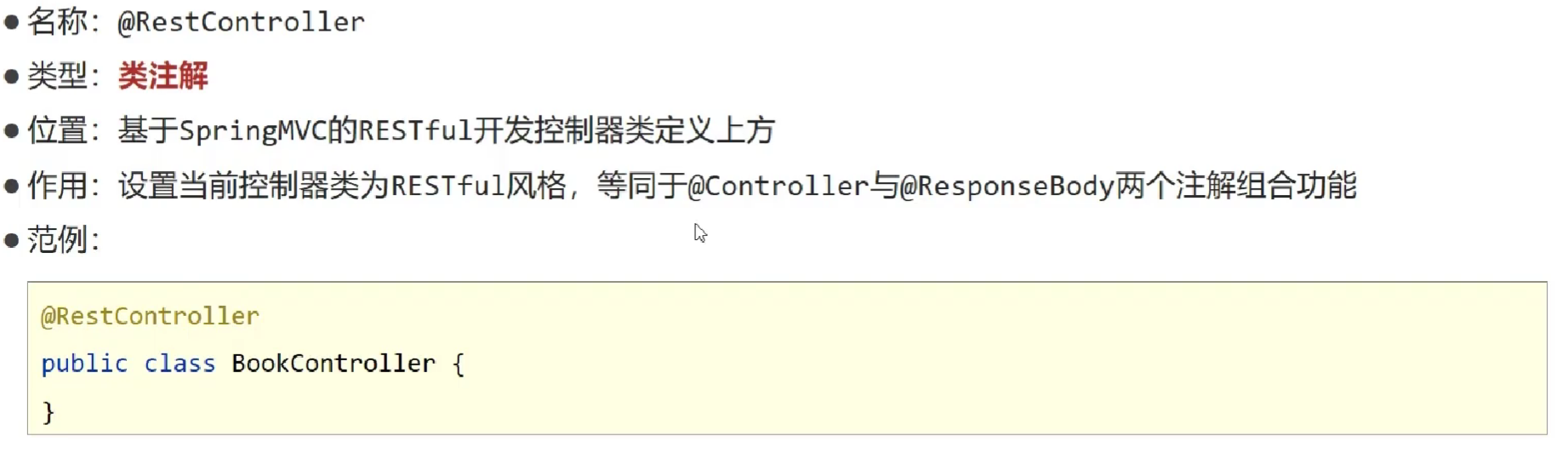
- 使用
@RestController注解开发 RESTful 风格
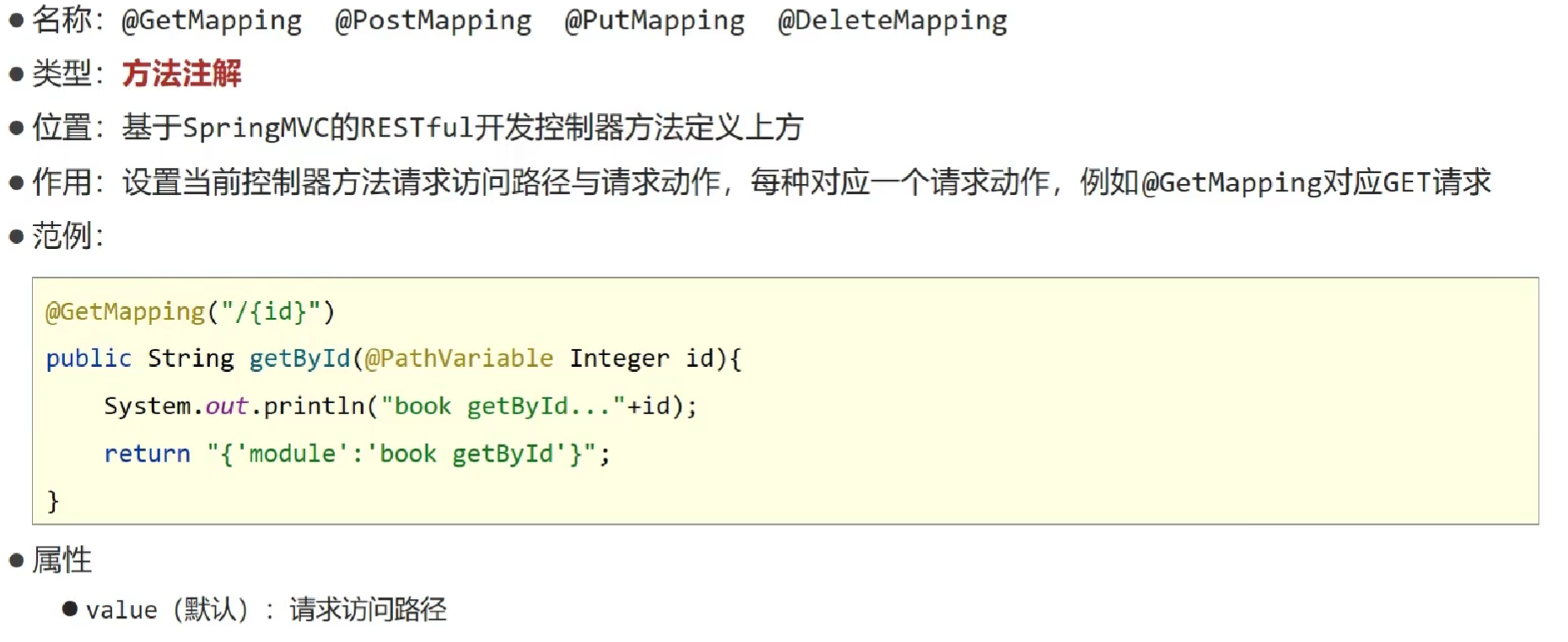
- 使用 @GetMapping @PostMapping @PutMapping @DeleteMapping 简化
@RequestMapping注解开发
# 12 - 教你一招:复制模块
- 原则
保留工程基础结构
抹掉原始工程痕迹
小结:
- 在工作空间中复制对应工程,并修改工程名称
- 删除与 Idea 相关配置文件,仅保留 src 目录与 pom.xml 文件
- 修改 pom.xml 文件中的 artifactId 与新工程 / 模块名相同
- 删除 name 标签(可选)
- 保留备份工程供后期使用
# 13 - 属性配置方式
-
修改服务器端口
-
SpringBoot 默认配置文件 application.properties,通过键值对配置对应属性
-
修改配置
修改服务器端口 ```bash# 服务器端口配制
server.port=80
小结:
- SpringBoot 默认配置文件 application.properties
# 14 - 基础配置
- 修改配置
修改服务器端口
server.port=80
关闭运行日志图标(banner)
spring.main.banner-mode=off
设置日志相关
logging.level.root=debug
# 服务器端口配置
server.port=80
# 修改banner
# spring.main.banner-mode=off
# spring.banner.image.location=logo.png
# 日志
logging.level.root=info
- SpringBoot 内置属性查询
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/application-properties.html#application-properties
官方文档中参考文档第一项:Application Propertie
小结:
- SpringBoot 中导入对应 starter 后,提供对应配置属性
- 书写 SpringBoot 配置采用关键字 + 提示形式书写
# 15-3 种配置文件类型
-
配置文件格式
-
SpringBoot 提供了多种属性配置方式
- application.properties
server.port=80
- application.yml
server:
port: 81
- application.yaml
server:
port: 82
小结:
- SpringBoot 提供了 3 种配置文件的格式
properties(传统格式 / 默认格式)
yml(主流格式)
yaml
# 16 - 配置文件加载优先级
- SpringBoot 配置文件加载顺序
application.properties > application.yml > application.yaml - 常用配置文件种类
application.yml
小结:
- 配置文件间的加载优先级
properties(最高)
yml
yaml(最低) - 不同配置文件中相同配置按照加载优先级相互覆盖 (高优先级配置内容会覆盖低优先级配置内容),不同配置文件中不同配置全部保留
# 17 - 教你一招:属性提示消失解决方案
小结:
- 指定 SpringBoot 配置文件
Setting → Project Structure → Facets
选中对应项目 / 工程
Customize Spring Boot
选择配置文件
# 18-yaml 数据格式
# yaml
- YAML(YAML Ain’t Markup Language),一种数据序列化格式
-
优点:
- 容易阅读
- 容易与脚本语言交互
- 以数据为核心,重数据轻格式
-
YAML 文件扩展名
- .yml(主流)
- .yaml
# yaml 语法规则
# 基本语法
key: value-> value 前面一定要有空格- 大小写敏感
- 属性层级关系使用多行描述,每行结尾使用冒号结束
- 使用缩进表示层级关系,同层级左侧对齐,只允许使用空格(不允许使用 Tab 键)
- 属性值前面添加空格(属性名与属性值之间使用冒号 + 空格作为分隔)
#表示注释- 核心规则:数据前面要加空格与冒号隔开
server:
servlet:
context-path: /hello
port: 82
# 数据类型
- 字面值表示方式
# 字面值表示方式
boolean: TRUE #TRUE,true,True,FALSE,false , False 均可
float: 3.14 #6.8523015e+5 # 支持科学计数法
int: 123 #0b1010_0111_0100_1010_1110 # 支持二进制、八进制、十六进制
# null: ~ # 使用 ~ 表示 null
string: HelloWorld # 字符串可以直接书写
string2: "Hello World" # 可以使用双引号包裹特殊字符
date: 2018-02-17 # 日期必须使用 yyyy-MM-dd 格式
datetime: 2018-02-17T15:02:31+08:00 # 时间和日期之间使用 T 连接,最后使用 + 代表时区
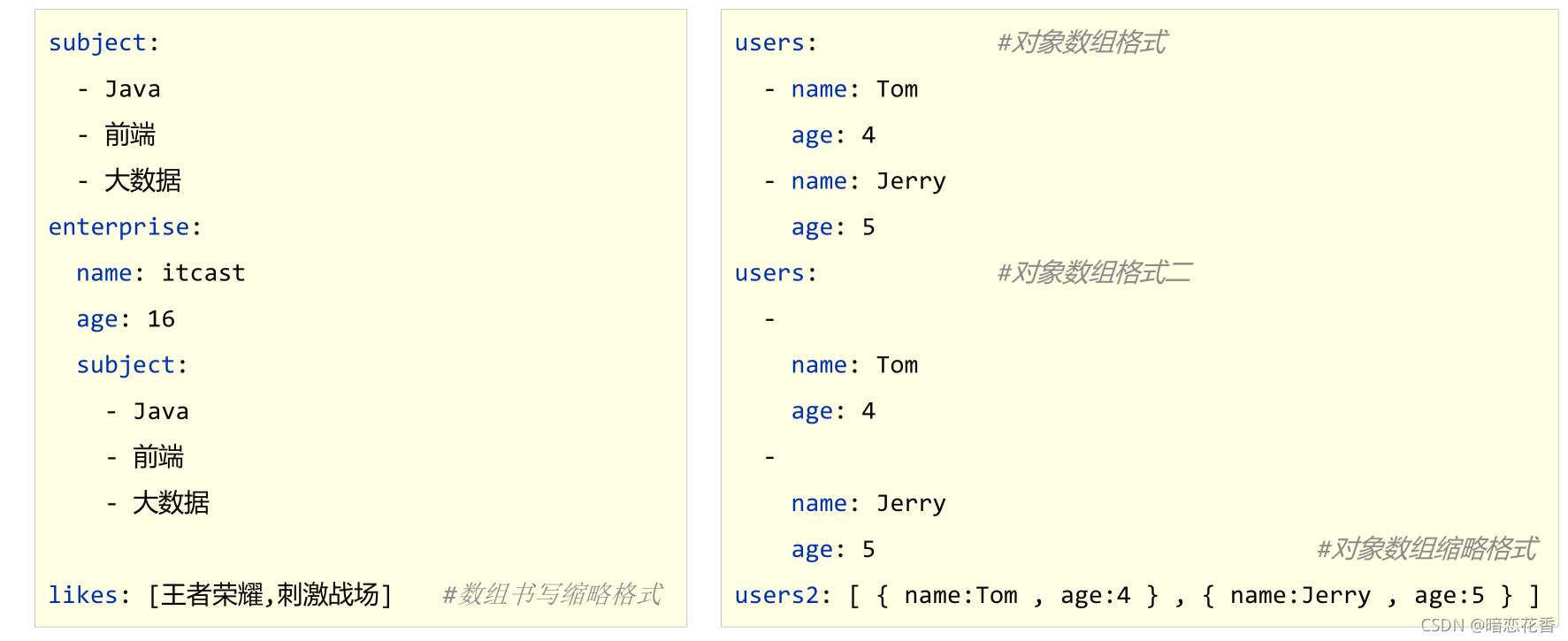
- 数组表示方式:在属性名书写位置的下方使用减号作为数据开始符号,每行书写一个数据,减号与数据间空格分隔
`subject:
- Java
- 前端
- 大数据
enterprise:
name: zhangsan
age: 16
subject2:
- Java
- 前端
- 大数据
likes: [王者荣耀,刺激战场] # 数组书写缩略格式
users: # 对象数组格式
- name: Tom
age: 4
- name: Jerry
age: 5
users2: # 对象数组格式二
-
name: Tom
age: 4
-
name: Jerry
age: 5
# 对象数组缩略格式
users3: [ { name:Tom , age:4 } , { name:Jerry , age:5 } ]`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
小结:
1. yaml语法规则
大小写敏感
属性层级关系使用多行描述,每行结尾使用冒号结束
使用缩进表示层级关系,同层级左侧对齐,只允许使用空格(不允许使用Tab键)
属性值前面添加空格(属性名与属性值之间使用冒号+空格作为分隔)
# 表示注释
2. 注意属性名冒号后面与数据之间有一个空格
3. 字面值、对象数据格式、数组数据格式(略)
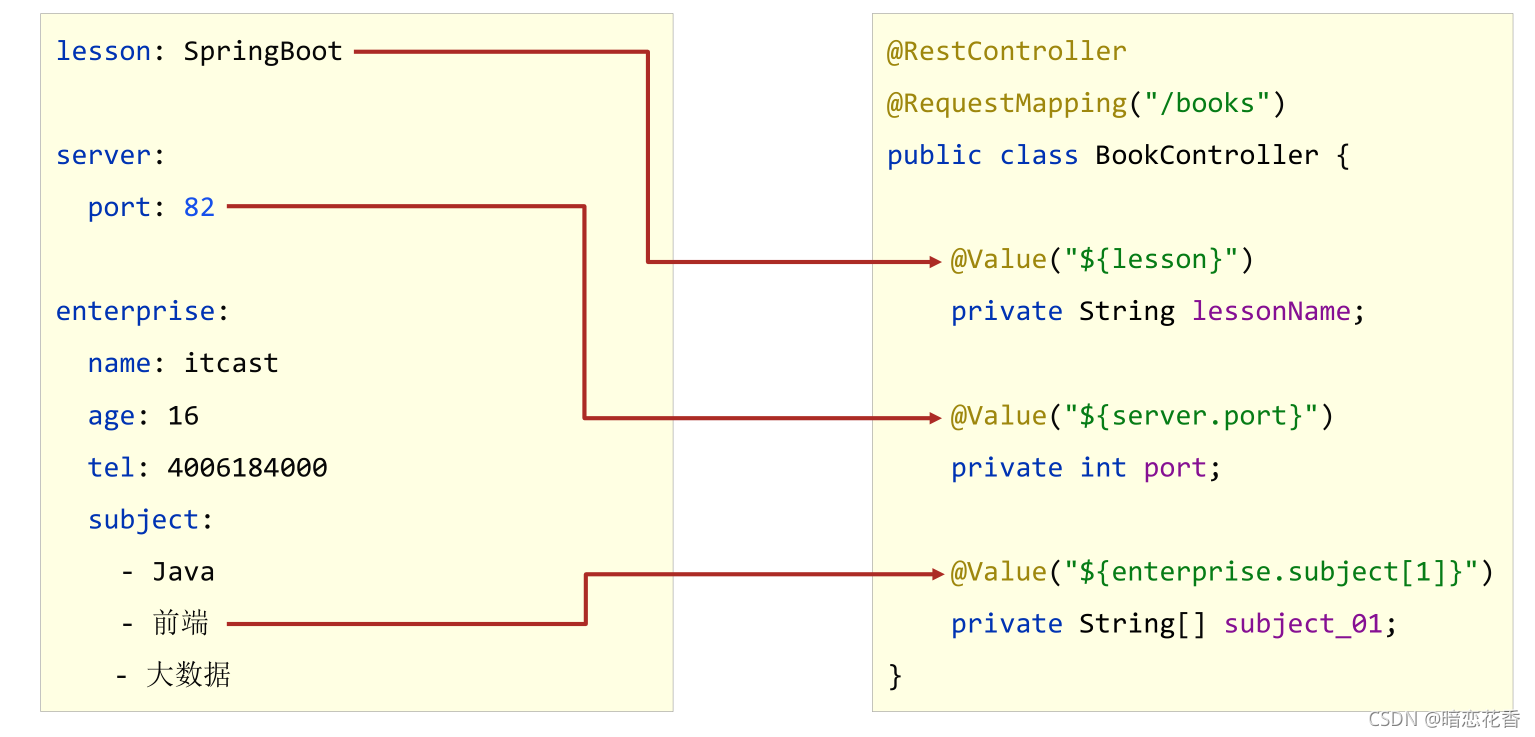
# 19 - 读取 yaml 单一属性数据
- 使用 @Value 读取单个数据,属性名引用方式:${一级属性名。二级属性名……}
@Value("${country}")
private String country1;
@Value("${user.age}")
private String age1;
@Value("${likes[1]}")
private String likes1;
@Value("${users[1].name}")
private String name1;
@GetMapping
public String getById() {
System.out.println("springboot is running2...");
System.out.println("country1=>" + country1);
System.out.println("age1=>" + age1);
System.out.println("likes1=>" + likes1);
System.out.println("name1=>" + name1);
return "springboot is running2...";
}
小结:
- 使用 @Value 配合 SpEL 读取单个数据
- 如果数据存在多层级,依次书写层级名称即可
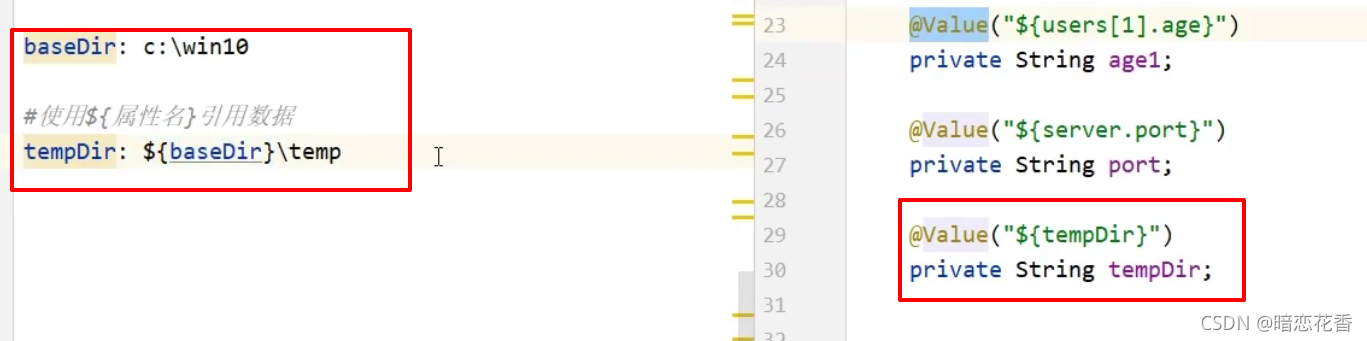
# 20-yaml 文件中的变量引用
-
在配置文件中可以使用属性名引用方式引用属性
-
属性值中如果出现转移字符,需要使用双引号包裹
小结:
- 在配置文件中可以使用 ${属性名} 方式引用属性值
- 如果属性中出现特殊字符,可以使用双引号包裹起来作为字符解析
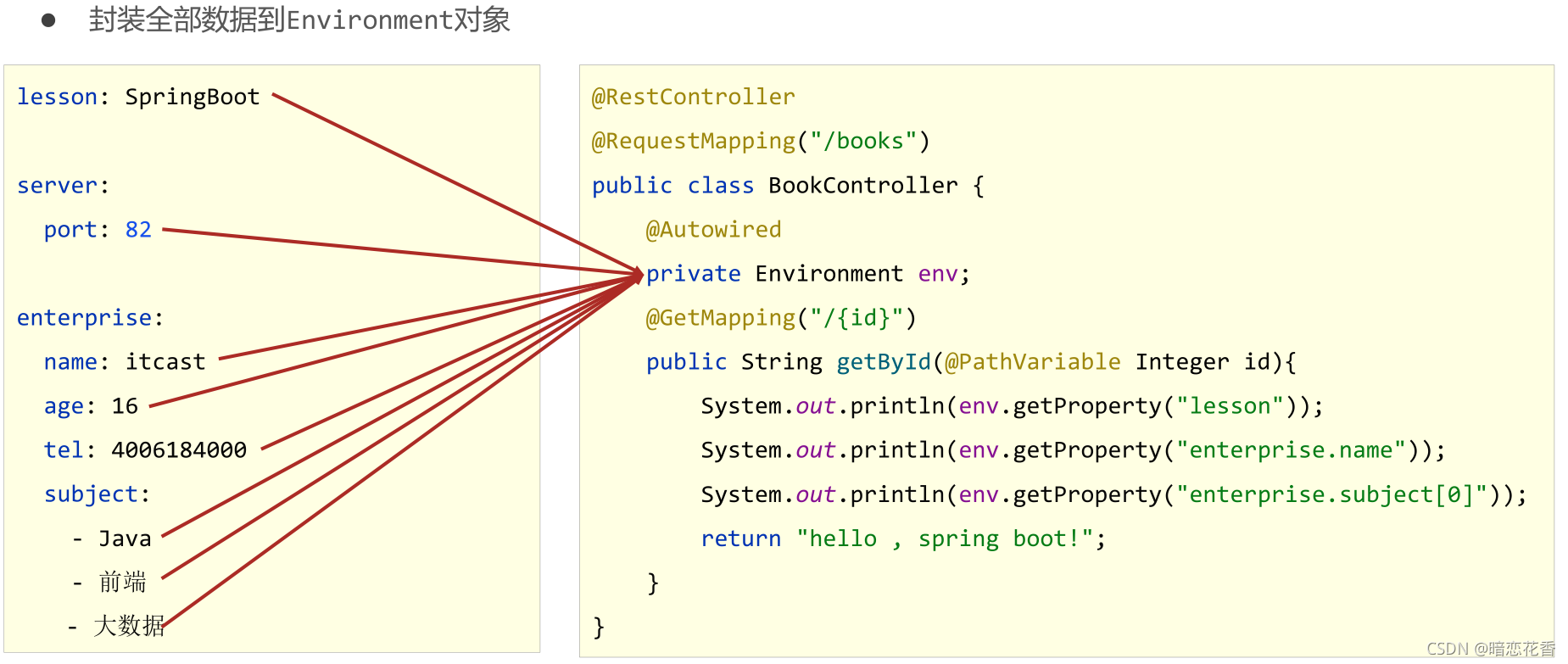
# 21 - 读取 yaml 全部属性数据
-
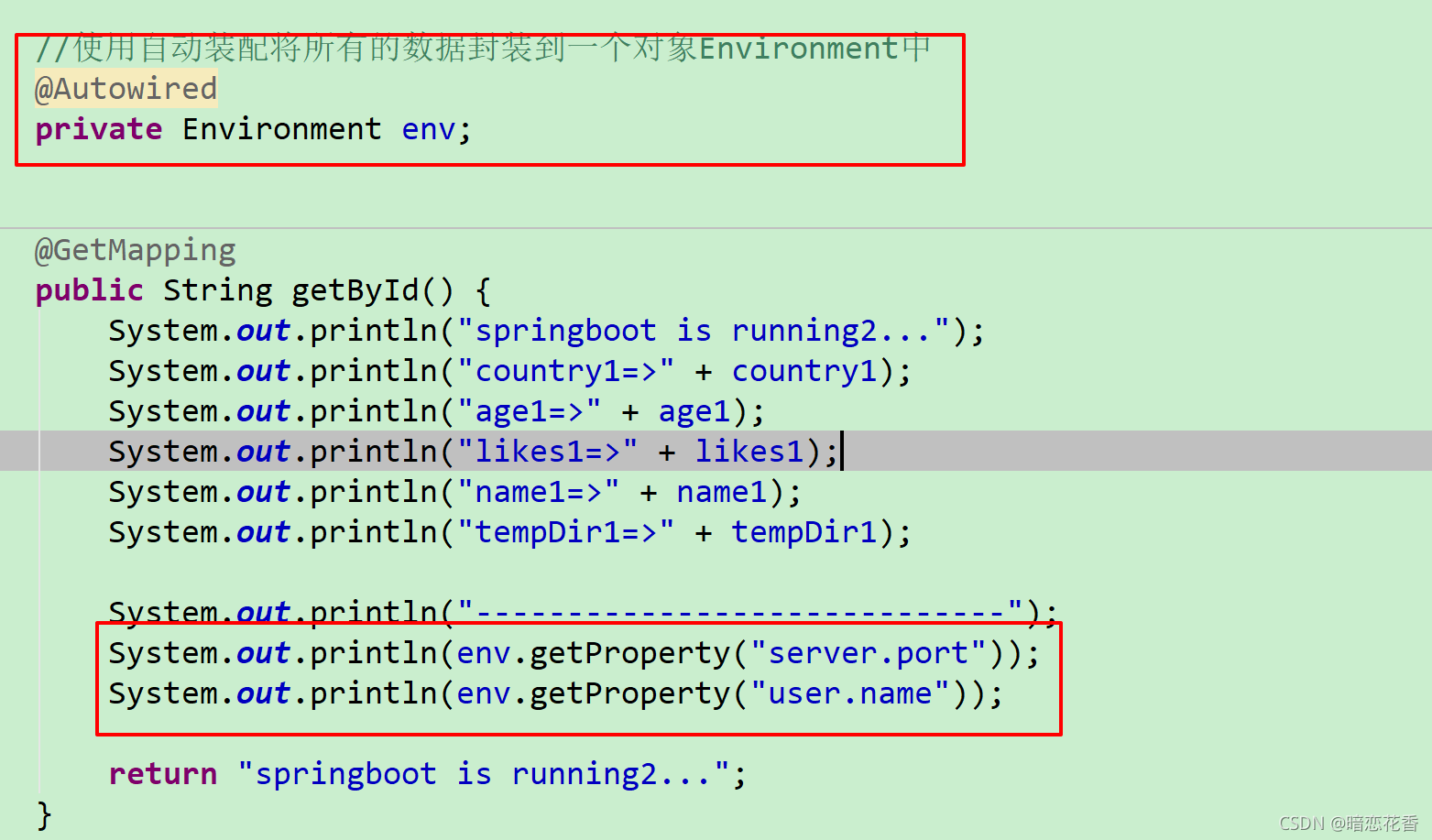
封装全部数据到 Environment 对象
-
注意 要导这个 包
-
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
小结:
- 使用 Environment 对象封装全部配置信息
- 使用 @Autowired 自动装配数据到 Environment 对象中
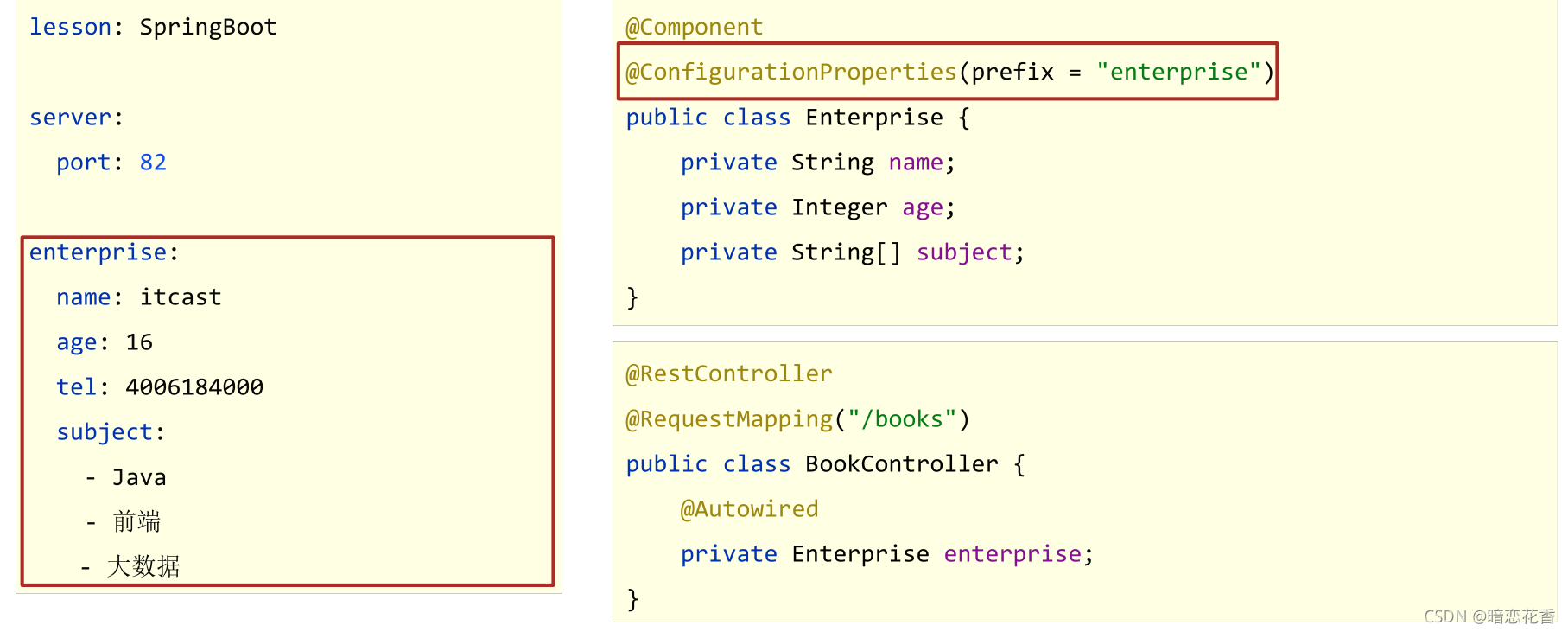
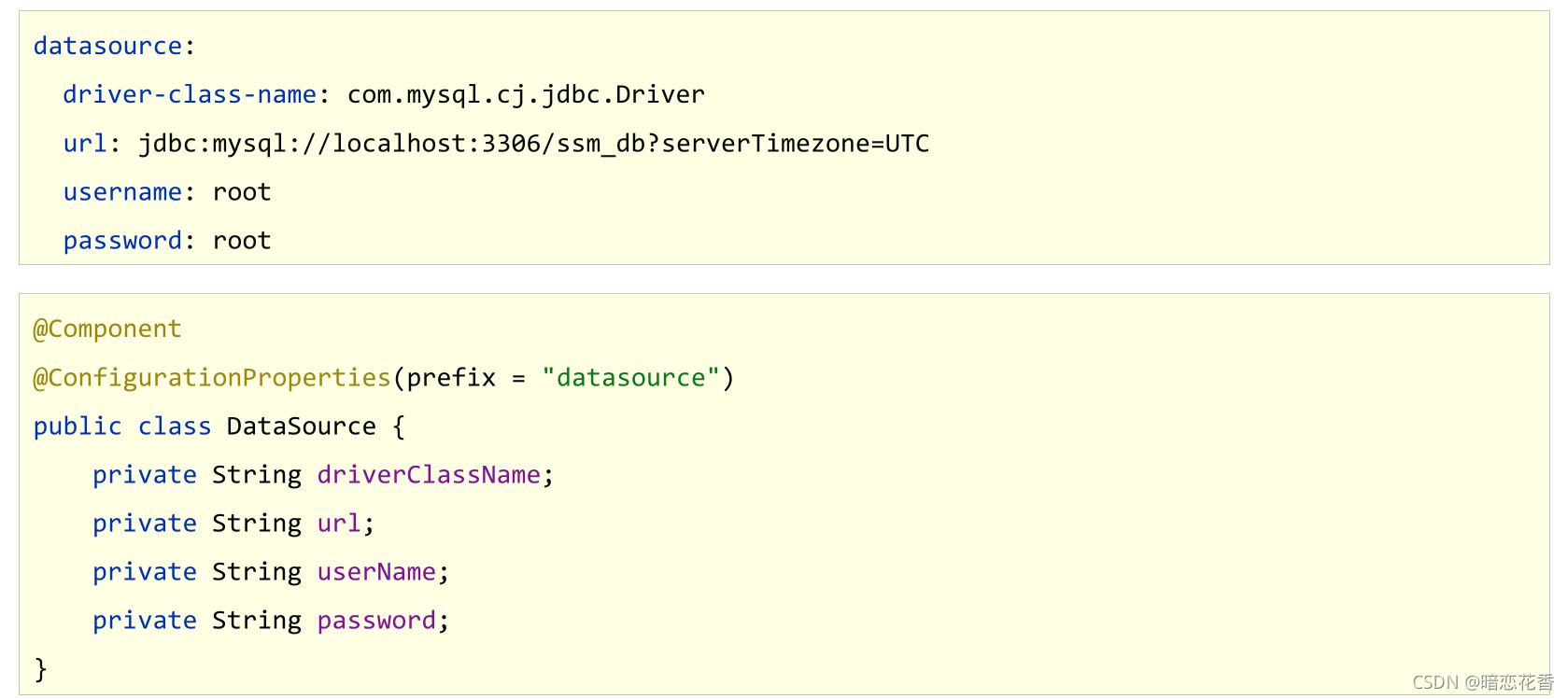
# 22 - 读取 yaml 引用类型属性数据
-
自定义对象封装指定数据
-
自定义对象封装指定数据的作用
# 创建类,用于封装下面的数据
# 由spring帮我们去加载数据到对象中,一定要告诉spring加载这组信息
# 使用时候从spring中直接获取信息使用
datasource:
driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost/springboot_db
username: root
password: root666123
//1.定义数据模型封装yaml文件中对应的数据
//2.定义为spring管控的bean
@Component
//3.指定加载的数据
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "datasource")
public class MyDataSource {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
//省略get/set/tostring 方法
}
使用自动装配封装指定数据
@Autowired
private MyDataSource myDataSource;
输出查看
System.out.println(myDataSource);
小结:
- 使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解绑定配置信息到封装类中
- 封装类需要定义为 Spring 管理的 bean,否则无法进行属性注入
# 23-SpringBoot 整合 JUnit
- 添加 Junit 的起步依赖 Spring Initializr 创建时自带
<!--测试的起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
- SpringBoot 整合 JUnit
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot07JunitApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@Test
public void testSave(){
bookService.save();
}
}
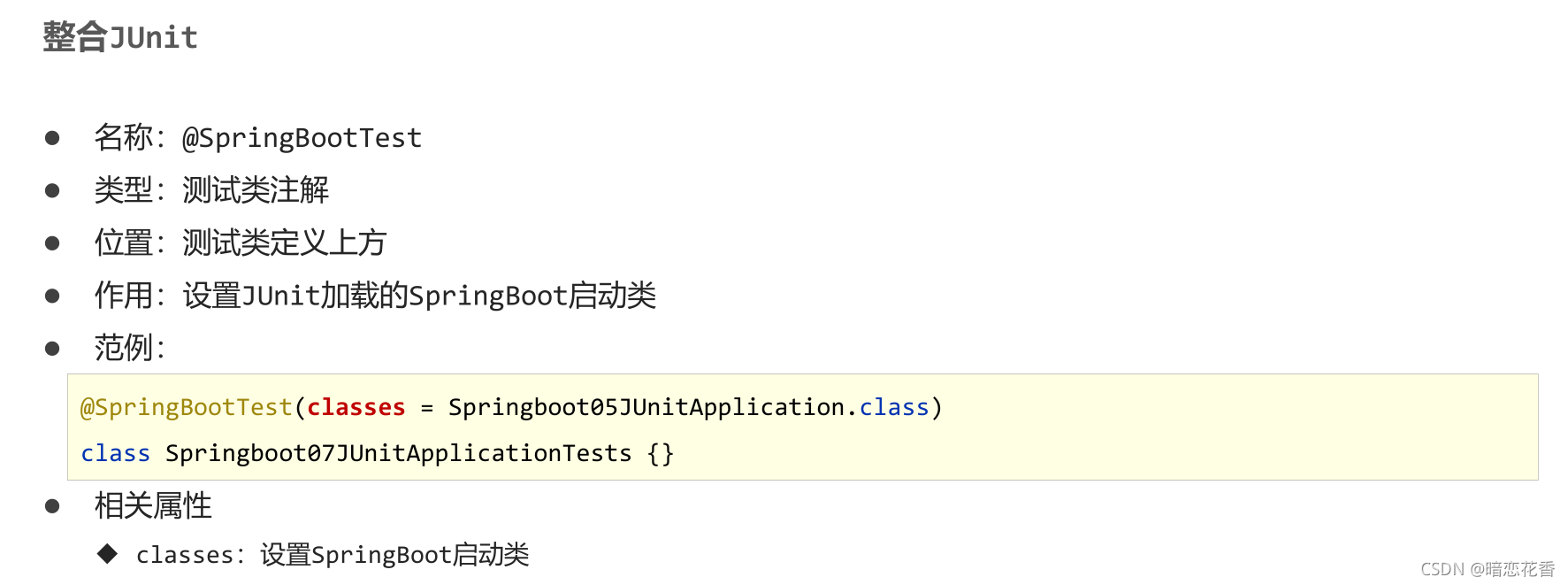
- @SpringBootTest
名称:@SpringBootTest
类型:测试类注解
位置:测试类定义上方
作用:设置 JUnit 加载的 SpringBoot 启动类
范例:
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot05JUnitApplicationTests {}
小结:
- 导入测试对应的 starter
- 测试类使用 @SpringBootTest 修饰
- 使用自动装配的形式添加要测试的对象
# 24 - 整合 JUnit——classes 属性
@SpringBootTest(classes = Springboot04JunitApplication.class)
//@ContextConfiguration(classes = Springboot04JunitApplication.class)
class Springboot04JunitApplicationTests {
//1.注入你要测试的对象
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//2.执行要测试的对象对应的方法
bookDao.save();
System.out.println("two...");
}
}
注意:
- 如果测试类在 SpringBoot 启动类的包或子包中,可以省略启动类的设置,也就是省略 classes 的设定
小结:
- 测试类如果存在于引导类所在包或子包中无需指定引导类
- 测试类如果不存在于引导类所在的包或子包中需要通过 classes 属性指定引导类
# 25-SpringBoot 整合 MyBatis
①:创建新模块,选择 Spring 初始化,并配置模块相关基础信息
②:选择当前模块需要使用的技术集(MyBatis、MySQL)
③:设置数据源参数
#DB Configuration:
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db
username: root
password: 123456
④:创建 user 表
在 springboot_db 数据库中创建 user 表
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for `user`
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=10 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of user
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('1', 'zhangsan', '123', '张三');
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES ('2', 'lisi', '123', '李四');
⑤:创建实体 Bean
public class User {
// 主键
private Long id;
// 用户名
private String username;
// 密码
private String password;
// 姓名
private String name;
//此处省略getter,setter,toString方法 .. ..
}
⑥: 定义数据层接口与映射配置
@Mapper
public interface UserDao {
@Select("select * from user")
public List<User> getAll();
}
⑦:测试类中注入 dao 接口,测试功能
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot05MybatisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
List<User> userList = userDao.getAll();
System.out.println(userList);
}
}
⑧:运行如下
[User{id=1, username='zhangsan', password='123', name='张三'}, User{id=2, username='lisi', password='123', name='李四'}]
总结:
- 勾选 MyBatis 技术,也就是导入 MyBatis 对应的 starter
- 数据库连接相关信息转换成配置
- 数据库 SQL 映射需要添加 @Mapper 被容器识别到
# 26-SpringBoot 整合 MyBatis 常见问题处理
SpringBoot 版本低于 2.4.3 (不含),Mysql 驱动版本大于 8.0 时,需要在 url 连接串中配置时区
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC
或在 MySQL 数据库端配置时区解决此问题
1.MySQL 8.X 驱动强制要求设置时区
- 修改 url,添加 serverTimezone 设定
- 修改 MySQL 数据库配置(略)
2. 驱动类过时,提醒更换为 com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# 27-SpringBoot 整合 MyBatisPlus
①:手动添加 SpringBoot 整合 MyBatis-Plus 的坐标,可以通过 mvnrepository 获取
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3</version>
</dependency>
注意事项:由于 SpringBoot 中未收录 MyBatis-Plus 的坐标版本,需要指定对应的 Version
②:定义数据层接口与映射配置,继承 BaseMapper
@Mapper
public interface UserDao extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
③:其他同 SpringBoot 整合 MyBatis
(略)
④:测试类中注入 dao 接口,测试功能
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot06MybatisPlusApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
List<User> users = userDao.selectList(null);
System.out.println(users);
}
}
⑤: 运行如下:
[User{id=1, username='zhangsan', password='123', name='张三'}, User{id=2, username='lisi', password='123', name='李四'}]
注意:如果你的数据库表有前缀要在 application.yml 添加如下配制
#设置Mp相关的配置
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: tbl_
小结:
1. 手工添加 MyBatis-Plus 对应的 starter
2. 数据层接口使用 BaseMapper 简化开发
3. 需要使用的第三方技术无法通过勾选确定时,需要手工添加坐标
# 28-SpringBoot 整合 Druid
①: 导入 Druid 对应的 starter
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>
②: 指定数据源类型 (这种方式只需导入一个 Druid 的坐标)
#DB Configuration:
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
或者 变更 Druid 的配置方式 (推荐) 这种方式需要导入 Druid 对应的 starter
spring:
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
小结:
1. 整合 Druid 需要导入 Druid 对应的 starter
2. 根据 Druid 提供的配置方式进行配置
3. 整合第三方技术通用方式
- 导入对应的 starter
- 根据提供的配置格式,配置非默认值对应的配置项
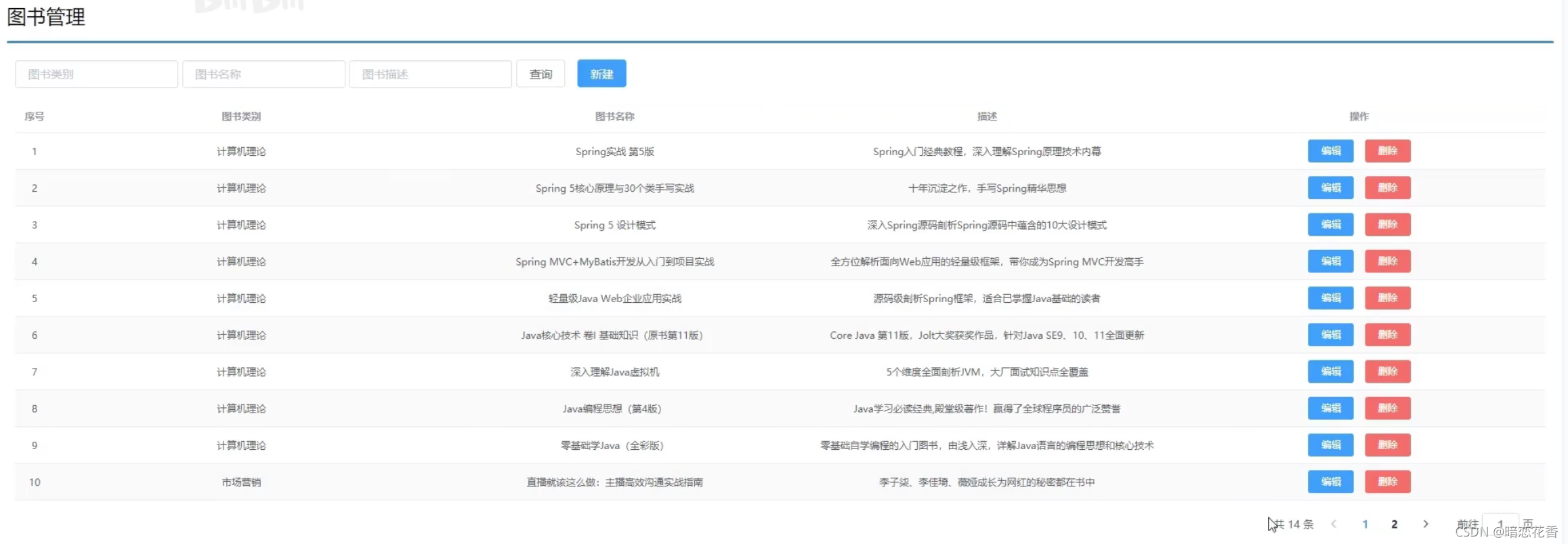
# 29-SSMP 整合案例制作分析
# 案例效果演示:
# 案例实现方案分析与流程解析
1. 案例实现方案分析
实体类开发————使用Lombok快速制作实体类
Dao开发————整合MyBatisPlus,制作数据层测试类
Service开发————基于MyBatisPlus进行增量开发,制作业务层测试类
Controller开发————基于Restful开发,使用PostMan测试接口功能
Controller开发————前后端开发协议制作
页面开发————基于VUE+ElementUI制作,前后端联调,页面数据处理,页面消息处理
列表、新增、修改、删除、分页、查询
项目异常处理
按条件查询————页面功能调整、Controller修正功能、Service修正功能
2. SSMP案例制作流程解析
先开发基础CRUD功能,做一层测一层
调通页面,确认异步提交成功后,制作所有功能
添加分页功能与查询功能
# 30 - 模块创建
pom.xml
`<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
# tbl_book.sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `tbl_book`;
CREATE TABLE `tbl_book` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`type` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`description` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=13 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of tbl_book
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('1', '计算机理论', 'Spring实战第5版', 'Spring入门经典教程,深入理解Spring原理技术内幕');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('2', '计算机理论', 'Spring 5核心原理与30个类手写实战', '十年沉淀之作,写Spring精华思想');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('3', '计算机理论', 'Spring 5设计模式', '深入Spring源码剖析Spring源码中蕴含的10大设计模式');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('4', '计算机理论', 'Spring MVC+ MyBatis开发从入门到项目实战', '全方位解析面向Web应用的轻量级框架,带你成为Spring MVC开发高手');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('5', '计算机理论', '轻量级Java Web企业应用实战', '源码级剖析Spring框架,适合已掌握Java基础的读者');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('6', '计算机理论', 'Java核心技术卷|基础知识(原书第11版)', 'Core Java第11版,Jolt大奖获奖作品,针对Java SE9、10、 11全面更新');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('7', '计算机理论', '深入理解Java虚拟机', '5个维度全面剖析JVM,面试知识点全覆盖');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('8', '计算机理论', 'Java编程思想(第4版)', 'Java学习必读经典殿堂级著作!赢得了全球程序员的广泛赞誉');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('9', '计算机理论', '零基础学Java (全彩版)', '零基础自学编程的入门]图书,由浅入深,详解Java语言的编程思想和核心技术');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('10', '市场营销', '直播就该这么做:主播高效沟通实战指南', '李子柒、李佳琦、薇娅成长为网红的秘密都在书中');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('11', '市场营销', '直播销讲实战一本通', '和秋叶一起学系列网络营销书籍');
INSERT INTO `tbl_book` VALUES ('12', '市场营销', '直播带货:淘宝、天猫直播从新手到高手', '一本教你如何玩转直播的书, 10堂课轻松实现带货月入3W+');
小结:
-
勾选 SpringMVC 与 MySQL 坐标
-
修改配置文件为 yml 格式
-
设置端口为 80 方便访问 ```yaml
server:
port: 80
# 31 - 实体类快速开发(lombok)
- Lombok,一个 Java 类库,提供了一组注解,简化 POJO 实体类开发
<!--lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
- lombok 版本由 SpringBoot 提供,无需指定版本
- 常用注解:@Data
@Data
public class Book {
private Integer id;
private String type;
private String name;
private String description;
}
- 为当前实体类在编译期设置对应的 get/set 方法,toString 方法,hashCode 方法,equals 方法等
小结:
1. 实体类制作
2. 使用lombok简化开发
导入lombok无需指定版本,由SpringBoot提供版本
@Data注解
# 32 - 数据层标准开发(基础 CRUD)
- 导入 MyBatisPlus 与 Druid 对应的 starter
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.6</version>
</dependency>
- 配置数据源与 MyBatisPlus 对应的基础配置(id 生成策略使用数据库自增策略)
# druid 数据源配制
spring:
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_db?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: 123456
# mybatis-plus
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: tbl_
id-type: auto # 主键策略
- 继承 BaseMapper 并指定泛型
@Mapper
public interface BookDao extends BaseMapper<Book> {
/**
* 查询一个
* 这是 Mybatis 开发
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Select("select * from tbl_book where id = #{id}")
Book getById(Integer id);
}
- 制作测试类测试结果
`@SpringBootTest
public class BookDaoTestCase {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Test
void testGetById() {
System.out.println(bookDao.getById(1));
System.out.println(bookDao.selectById(1));
}
@Test
void testSave() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setType("测试数据123");
book.setName("测试数据123");
book.setDescription("测试数据123");
bookDao.insert(book);
}
@Test
void testUpdate() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(13);
book.setType("测试数据asfd");
book.setName("测试数据123");
book.setDescription("测试数据123");
bookDao.updateById(book);
}
@Test
void testDelete() {
bookDao.deleteById(13);
}
@Test
void testGetAll() {
System.out.println(bookDao.selectList(null));
}
@Test
void testGetPage() {
}
@Test
void testGetBy() {
}
}`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
* 40
* 41
* 42
* 43
* 44
* 45
* 46
* 47
* 48
* 49
* 50
小结:
- 手工导入 starter 坐标(2 个)
- 配置数据源与 MyBatisPlus 对应的配置
- 开发 Dao 接口(继承 BaseMapper)
- 制作测试类测试 Dao 功能是否有效
# 33 - 开启 MP 运行日志
- 为方便调试可以开启 MyBatisPlus 的日志
# mybatis-plus
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: tbl_
id-type: auto # 主键策略
configuration:
# 开启MyBatisPlus的日志
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
小结:
- 使用配置方式开启日志,设置日志输出方式为标准输出
# 34 - 分页
- 分页操作需要设定分页对象 IPage
@Test
void testGetPage() {
IPage page = new Page(1, 5);
bookDao.selectPage(page, null);
}
-
IPage 对象中封装了分页操作中的所有数据
数据
当前页码值
每页数据总量
最大页码值
数据总量 -
分页操作是在 MyBatisPlus 的常规操作基础上增强得到,内部是动态的拼写 SQL 语句,因此需要增强对应的功能,
使用 MyBatisPlus 拦截器实现
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
//1. 定义 Mp 拦截器
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
//2. 添加具体的拦截器 分页拦截器
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor());
return interceptor;
}
}
- 测试
@Test
void testGetPage() {
IPage page = new Page(1, 5);
bookDao.selectPage(page, null);
System.out.println(page.getCurrent());
System.out.println(page.getSize());
System.out.println(page.getPages());
System.out.println(page.getTotal());
System.out.println(page.getRecords());
}
小结:
- 使用 IPage 封装分页数据
- 分页操作依赖 MyBatisPlus 分页拦截器实现功能
- 借助 MyBatisPlus 日志查阅执行 SQL 语句
# 35 - 数据层标准开发(条件查询)
- 使用 QueryWrapper 对象封装查询条件,推荐使用 LambdaQueryWrapper 对象,所有查询操作封装成方法调用
@Test
void testGetBy2() {
LambdaQueryWrapper<Book> lambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
lambdaQueryWrapper.like(Book::getName, "Spring");
bookDao.selectList(lambdaQueryWrapper);
}
@Test
void testGetBy() {
QueryWrapper<Book> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name", "Spring");
bookDao.selectList(queryWrapper);
}
- 支持动态拼写查询条件
@Test
void testGetBy2() {
String name = "1";
LambdaQueryWrapper<Book> lambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//if (name != null) lambdaQueryWrapper.like(Book::getName,name);
lambdaQueryWrapper.like(Strings.isNotEmpty(name), Book::getName, name);
bookDao.selectList(lambdaQueryWrapper);
}
小结:
- 使用 QueryWrapper 对象封装查询条件
- 推荐使用 LambdaQueryWrapper 对象
- 所有查询操作封装成方法调用
- 查询条件支持动态条件拼装
# 36 - 业务层标准开发(基础 CRUD)
-
Service 层接口定义与数据层接口定义具有较大区别,不要混用
selectByUserNameAndPassword (String username,String password); 数据层接口
login (String username,String password); Service 层接口 -
接口定义
public interface BookService {
Boolean save(Book book);
Boolean update(Book book);
Boolean delete(Integer id);
Book getById(Integer id);
List<Book> getAll();
IPage<Book> getPage(int currentPage,int pageSize);
}
- 实现类定义
`@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Override
public Boolean save(Book book) {
return bookDao.insert(book) > 0;
}
@Override
public Boolean update(Book book) {
return bookDao.updateById(book) > 0;
}
@Override
public Boolean delete(Integer id) {
return bookDao.deleteById(id) > 0;
}
@Override
public Book getById(Integer id) {
return bookDao.selectById(id);
}
@Override
public List<Book> getAll() {
return bookDao.selectList(null);
}
@Override
public IPage<Book> getPage(int currentPage, int pageSize) {
IPage page = new Page(currentPage, pageSize);
bookDao.selectPage(page, null);
return page;
}
}`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
- 测试类定义
`@SpringBootTest
public class BookServiceTestCase {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@Test
void testGetById() {
System.out.println(bookService.getById(4));
}
@Test
void testSave() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setType("测试数据123");
book.setName("测试数据123");
book.setDescription("测试数据123");
bookService.save(book);
}
@Test
void testUpdate() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(14);
book.setType("测试数据asfd");
book.setName("测试数据123");
book.setDescription("测试数据123");
bookService.update(book);
}
@Test
void testDelete() {
bookService.delete(14);
}
@Test
void testGetAll() {
System.out.println(bookService.getAll());
}
@Test
void testGetPage() {
IPage<Book> page = bookService.getPage(2, 5);
System.out.println(page.getCurrent());
System.out.println(page.getSize());
System.out.println(page.getPages());
System.out.println(page.getTotal());
System.out.println(page.getRecords());
}
}`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
* 40
* 41
* 42
* 43
* 44
* 45
* 46
* 47
* 48
* 49
* 50
* 51
小结:
- Service 接口名称定义成业务名称,并与 Dao 接口名称进行区分
- 制作测试类测试 Service 功能是否有效
# 37 - 业务层快速开发(基于 MyBatisPlus 构建)
-
快速开发方案
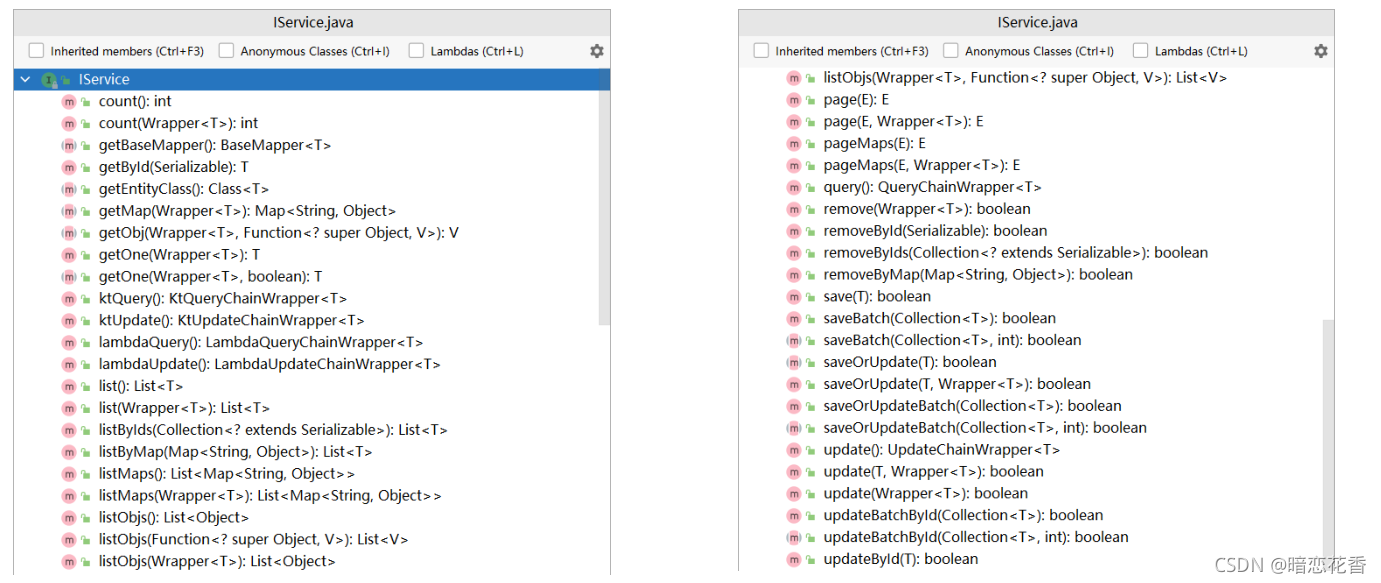
使用 MyBatisPlus 提供有业务层通用接口(ISerivce)与业务层通用实现类(ServiceImpl<M,T>)
在通用类基础上做功能重载或功能追加
注意重载时不要覆盖原始操作,避免原始提供的功能丢失
-
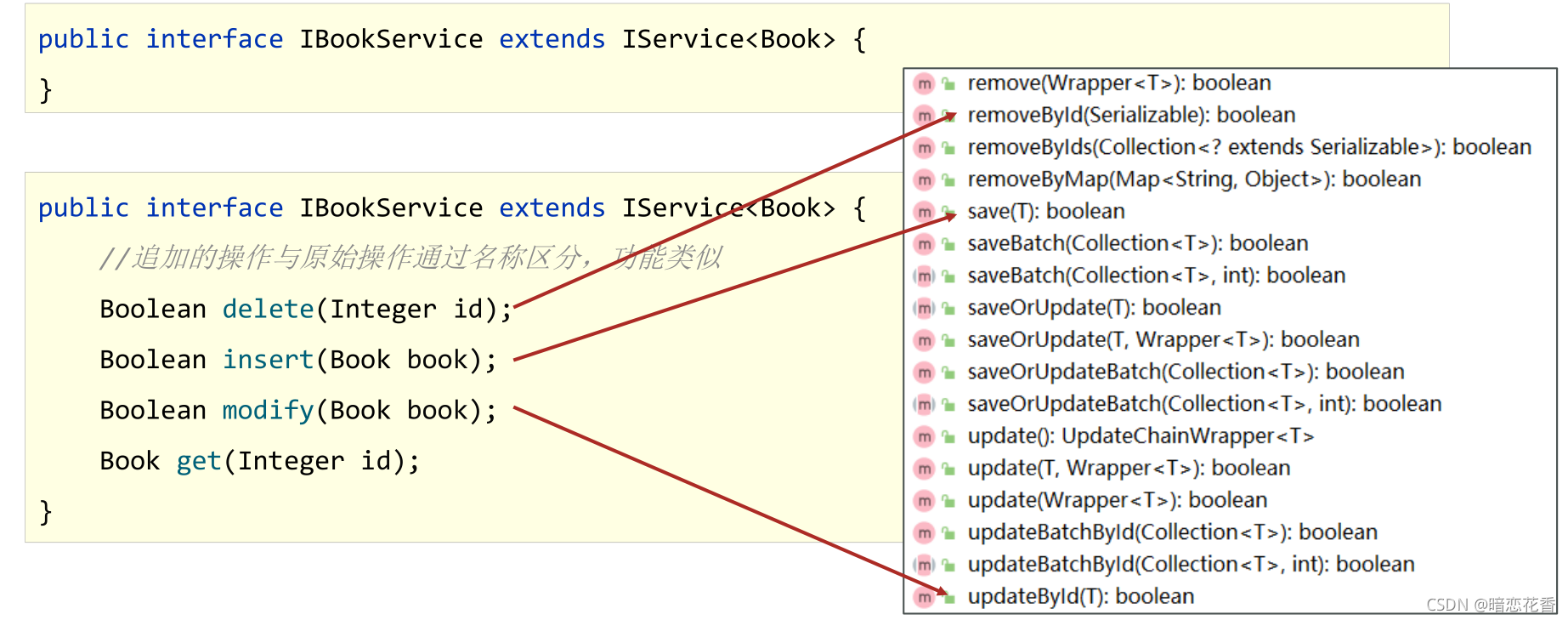
接口定义
public interface IBookService extends IService<Book> {
}
- 接口追加功能
public interface IBookService extends IService<Book> {
// 追加的操作与原始操作通过名称区分,功能类似
Boolean delete(Integer id);
Boolean insert(Book book);
Boolean modify(Book book);
Book get(Integer id);
}
- 实现类定义
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<BookDao, Book> implements IBookService {
}
- 实现类追加功能
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<BookDao, Book> implements IBookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
public Boolean insert(Book book) {
return bookDao.insert(book) > 0;
}
public Boolean modify(Book book) {
return bookDao.updateById(book) > 0;
}
public Boolean delete(Integer id) {
return bookDao.deleteById(id) > 0;
}
public Book get(Integer id) {
return bookDao.selectById(id);
}
}
- 测试类定义
`@SpringBootTest
public class BookServiceTest {
@Autowired
private IBookService bookService;
@Test
void testGetById() {
System.out.println(bookService.getById(4));
}
@Test
void testSave() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setType("测试数据123");
book.setName("测试数据123");
book.setDescription("测试数据123");
bookService.save(book);
}
@Test
void testUpdate() {
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(14);
book.setType("===========");
book.setName("测试数据123");
book.setDescription("测试数据123");
bookService.updateById(book);
}
@Test
void testDelete() {
bookService.removeById(14);
}
@Test
void testGetAll() {
System.out.println(bookService.list());
}
@Test
void testGetPage() {
IPage<Book> page = new Page<>(2, 5);
bookService.page(page);
System.out.println(page.getCurrent());
System.out.println(page.getSize());
System.out.println(page.getPages());
System.out.println(page.getTotal());
System.out.println(page.getRecords());
}
}`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
* 40
* 41
* 42
* 43
* 44
* 45
* 46
* 47
* 48
* 49
* 50
* 51
小结:
- 使用通用接口(ISerivce)快速开发 Service
- 使用通用实现类(ServiceImpl<M,T>)快速开发 ServiceImpl
- 可以在通用接口基础上做功能重载或功能追加
- 注意重载时不要覆盖原始操作,避免原始提供的功能丢失
# 38 - 表现层标准开发
- 基于 Restful 进行表现层接口开发
- 使用 Postman 测试表现层接口功能
表现层开发
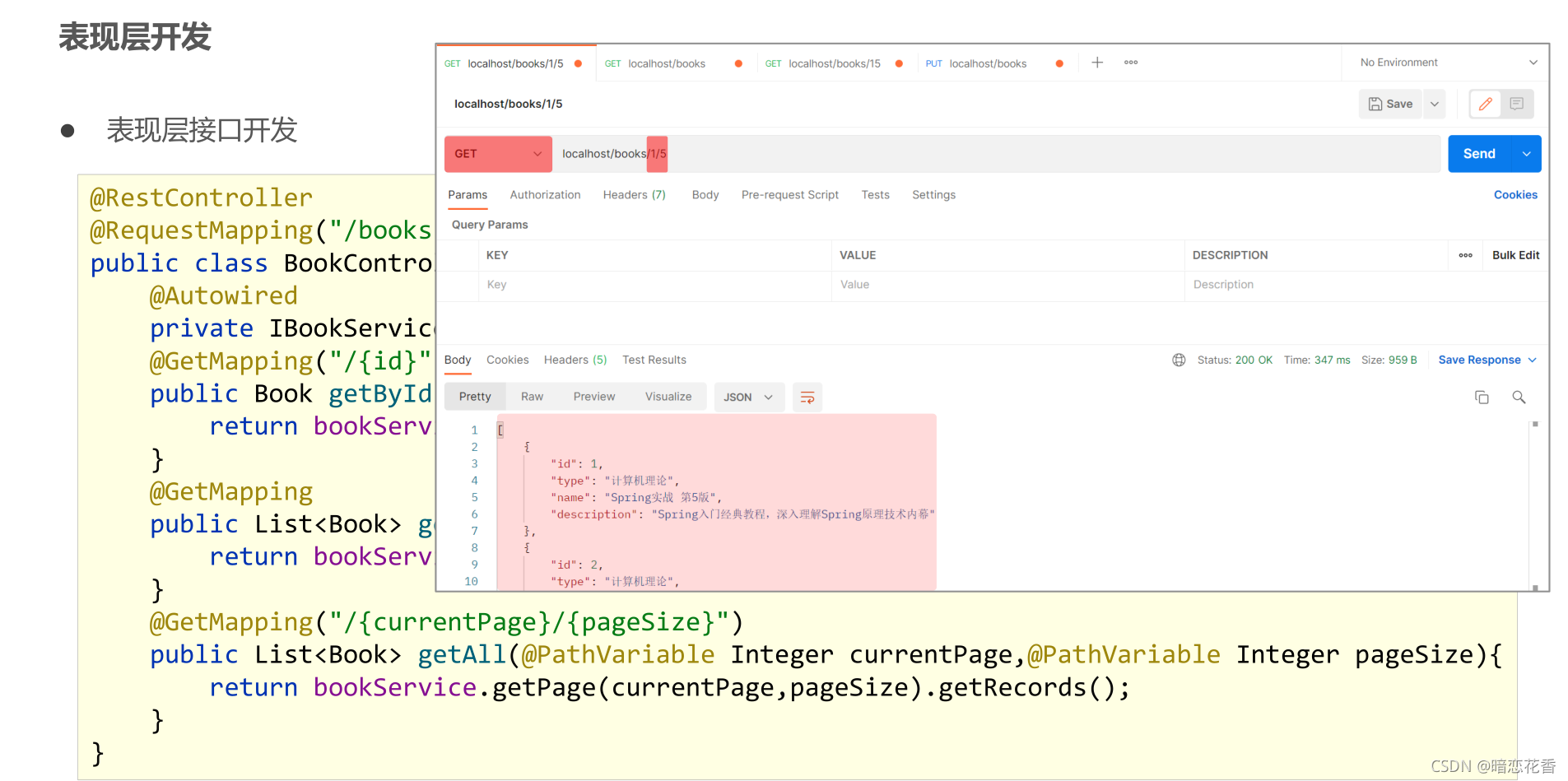
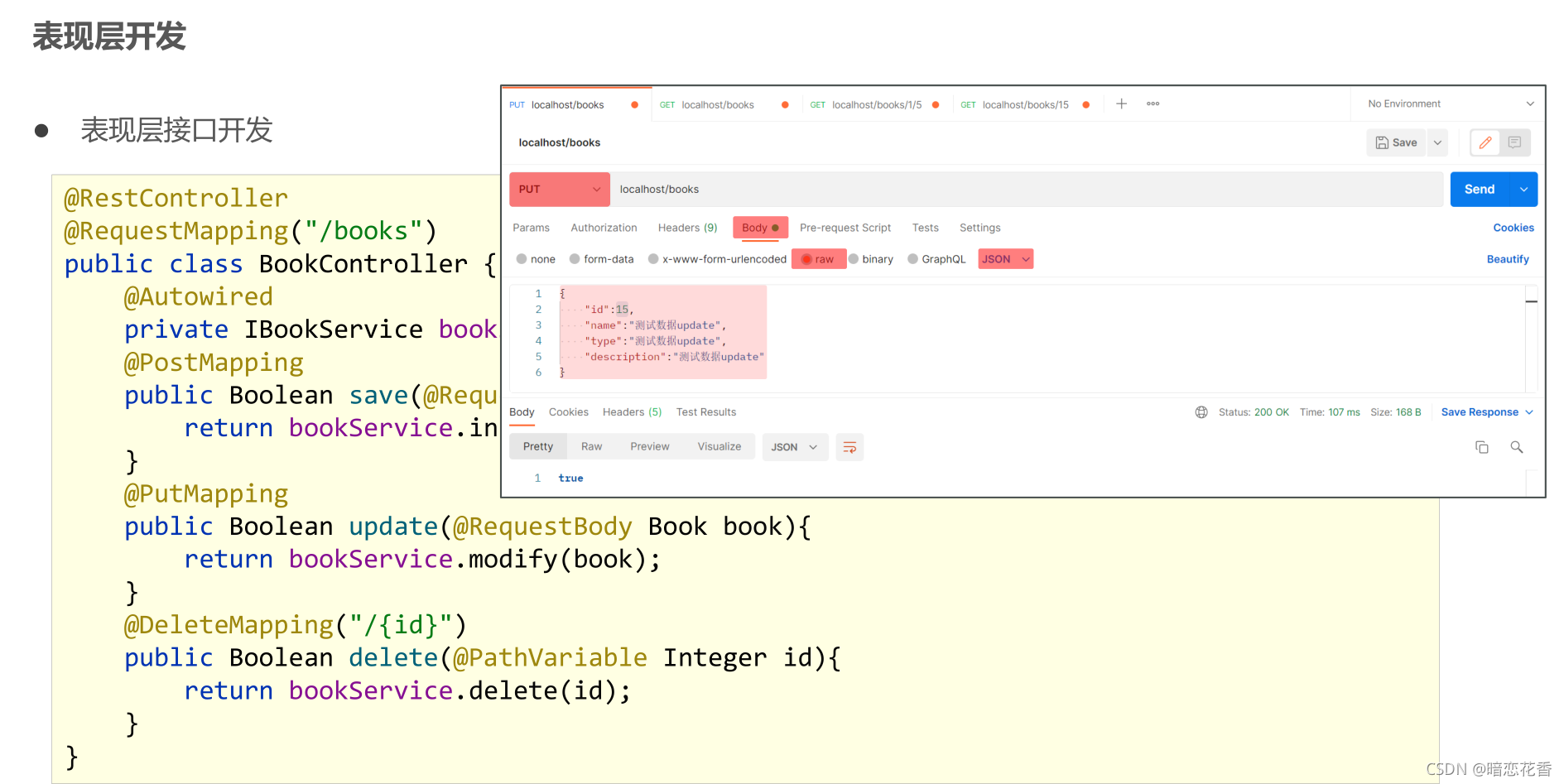
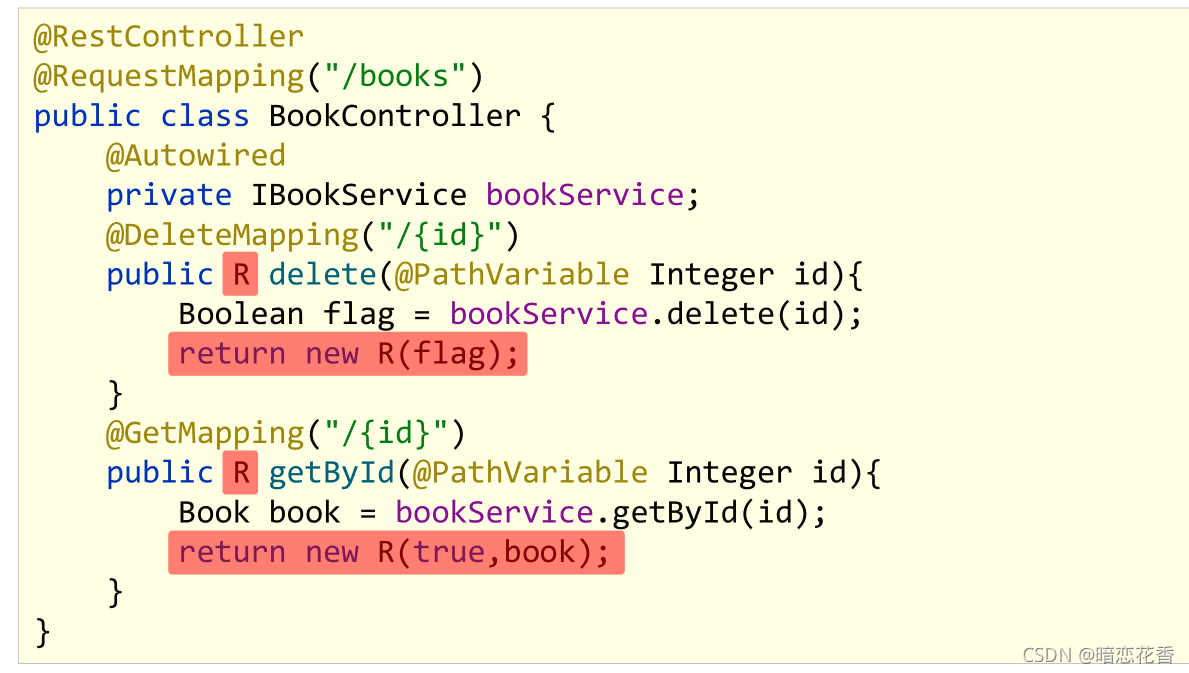
`@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private IBookService bookService;
@GetMapping
public List<Book> getAll() {
return bookService.list();
}
@PostMapping
public Boolean save(@RequestBody Book book) {
return bookService.save(book);
}
@PutMapping
public Boolean update(@RequestBody Book book) {
return bookService.modify(book);
}
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public Boolean delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return bookService.delete(id);
}
@GetMapping("{id}")
public Book getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return bookService.getById(id);
}
@GetMapping("{currentPage}/{pageSize}")
public IPage<Book> getPage(@PathVariable Integer currentPage, @PathVariable int pageSize) {
return bookService.getPage(currentPage, pageSize);
}
}`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
添加 分页的业务层方法
IBookService
IPage<Book> getPage(int currentPage,int pageSize);
BookServiceImpl
@Override
public IPage<Book> getPage(int currentPage, int pageSize) {
IPage page = new Page(currentPage, pageSize);
bookDao.selectPage(page, null);
return page;
}
功能测试
小结:
- 基于 Restful 制作表现层接口
新增:POST
删除:DELETE
修改:PUT
查询:GET - 接收参数
实体数据:@RequestBody
路径变量:@PathVariable
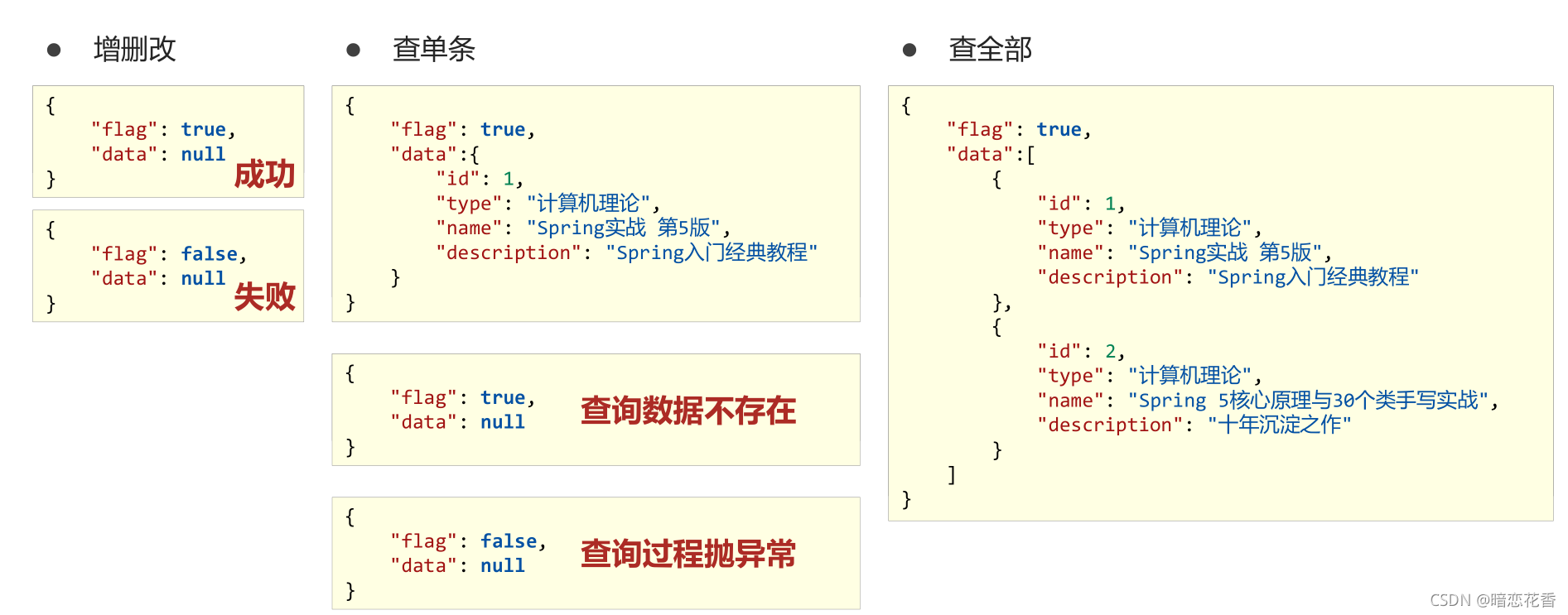
# 39 - 表现层数据一致性处理(R 对象)
-
之前的格式
-
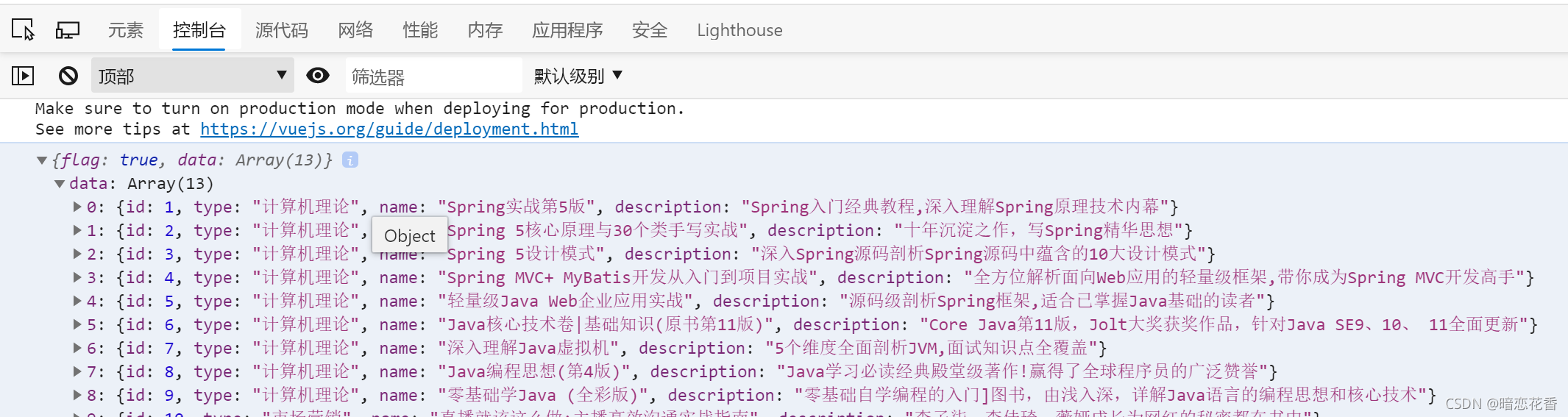
增加一个 data 属性,把数据全部封装到 data 里
当数据为 null 可能出现的问题
- 查询 id 不存在的数据,返回 null
- 查询过程中抛出异常,catch 中返回 null
-
增加 一个状态属性
-
设计表现层返回结果的模型类,用于后端与前端进行数据格式统一,也称为前后端数据协议
@Data
public class R {
private Boolean flag;
private Object data;
public R() {
}
/**
* 不返回数据的构造方法
*
* @param flag
*/
public R(Boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
/**
* 返回数据的构造方法
*
* @param flag
* @param data
*/
public R(Boolean flag, Object data) {
this.flag = flag;
this.data = data;
}
}
- 表现层接口统一返回值类型结果
`@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private IBookService bookService;
@GetMapping
public R getAll() {
return new R(true, bookService.list());
}
@PostMapping
public R save(@RequestBody Book book) {
return new R(bookService.save(book));
}
@PutMapping
public R update(@RequestBody Book book) {
return new R(bookService.modify(book));
}
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public R delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return new R(bookService.delete(id));
}
@GetMapping("{id}")
public R getById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return new R(true, bookService.getById(id));
}
@GetMapping("{currentPage}/{pageSize}")
public R getPage(@PathVariable Integer currentPage, @PathVariable int pageSize) {
return new R(true, bookService.getPage(currentPage, pageSize));
}
}`

* 1
* 2
* 3
* 4
* 5
* 6
* 7
* 8
* 9
* 10
* 11
* 12
* 13
* 14
* 15
* 16
* 17
* 18
* 19
* 20
* 21
* 22
* 23
* 24
* 25
* 26
* 27
* 28
* 29
* 30
* 31
* 32
* 33
* 34
* 35
* 36
* 37
* 38
* 39
小结:
- 设计统一的返回值结果类型便于前端开发读取数据
- 返回值结果类型可以根据需求自行设定,没有固定格式
- 返回值结果模型类用于后端与前端进行数据格式统一,也称为前
后端数据协议
# 40 - 前后端调用(axios 发送异步请求)
# 使用 VUE 的方法时提示报错:
Method definition shorthands are not supported by current JavaScript version
表示:该方法定义的缺陷是不支持当前的 JavaScript 版本,虽然可以程序可以正常运行,但是这个方法会出现红色的波浪线,很不爽
解决:
打开 File -> Settings -> Languages & Frameworks -> Javascript
把 JavaScript 版本为 ECMAScript 6 就可以了
- 前后端分离结构设计中页面归属前端服务器
- 单体工程中页面放置在 resources 目录下的 static 目录中(建议执行 clean)
- 前端发送异步请求,调用后端接口
//钩子函数,VUE对象初始化完成后自动执行
created() {
//调用查询全部数据的操作
this.getAll();
},
//列表
getAll() {
//发送异步请求
axios.get("/books").then((res)=>{
console.log(res.data);
})
},
小结:
- 单体项目中页面放置在 resources/static 目录下
- created 钩子函数用于初始化页面时发起调用
- 页面使用 axios 发送异步请求获取数据后确认前后端是否联通
# 41 - 列表功能
- 列表页
//列表
getAll() {
//发送异步请求
axios.get("/books").then((res) => {
//console.log(res.data);
this.dataList = res.data.data;
})
},
小结:
- 将查询数据返回到页面,利用前端数据双向绑定进行数据展示
# 42 - 添加功能
- 弹出添加窗口
// 弹出添加窗口
handleCreate() {
this.dialogFormVisible = true;
},
- 清除数据
//重置表单
resetForm() {
this.formData = {};
},
- 在弹出添加窗口时 清除数据
//弹出添加窗口
handleCreate() {
this.dialogFormVisible = true;
this.resetForm();
},
- 发送添加请求
//添加
handleAdd() {
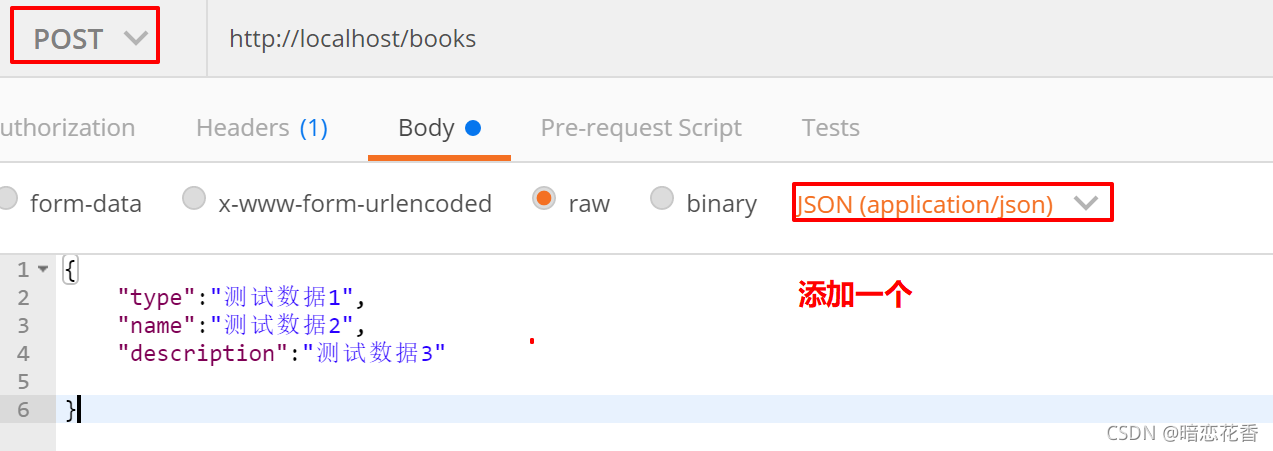
axios.post("/books", this.formData).then((res) => {
//判断当前操作是否成功
if (res.data.flag) {
//1.关闭弹层
this.dialogFormVisible = false;
this.$message.success("添加成功");
} else {
this.$message.error("添加失败");
}
}).finally(() => {
//2.重新加载数据
this.getAll();
})
},
- 取消添加
//取消
cancel() {
//1.关闭弹层
this.dialogFormVisible = false;
//2.提示用户
this.$message.info("当前操作取消");
},
小结:
- 请求方式使用 POST 调用后台对应操作
- 添加操作结束后动态刷新页面加载数据
- 根据操作结果不同,显示对应的提示信息
- 弹出添加 Div 时清除表单数据
# 43 - 删除功能
- 删除
// 删除
handleDelete(row) {
axios.delete("/books/" + row.id).then((res) => {
if (res.data.flag) {
this.$message.success("删除成功");
} else {
this.$message.error("删除失败");
}
}).finally(() => {
this.getAll();
});
}
- 加入确认删除对话框
// 删除
handleDelete(row) {
//1. 弹出提示框
this.$confirm("些操作永久删除当前信息,是否继续?", "提示", {type: "info"}).then(() => {
//2. 做删除业务
axios.delete("/books/" + row.id).then((res) => {
//判断当前操作是否成功
if (res.data.flag) {
this.$message.success("删除成功");
} else {
this.$message.error("删除失败");
}
}).finally(() => {
//2.重新加载数据
this.getAll();
})
}).catch(() => {
//3. 取消删除
this.$message.info("取消操作");
});
},
小结:
- 请求方式使用 Delete 调用后台对应操作
- 删除操作需要传递当前行数据对应的 id 值到后台
- 删除操作结束后动态刷新页面加载数据
- 根据操作结果不同,显示对应的提示信息
- 删除操作前弹出提示框避免误操作
# 44 修改功能(加载数据)
- 弹出修改窗口
//弹出编辑窗口
handleUpdate(row) {
axios.get("/books/" + row.id).then((res) => {
if (res.data.flag && res.data.data != null) {
// 展示弹层,加载数据
this.dialogFormVisible4Edit = true;
this.formData = res.data.data;
} else {
this.$message.error("数据同步失败,自动刷新");
}
}).finally(() => {
//重新加载数据
this.getAll();
});
},
- 删除消息维护
// 删除
handleDelete(row) {
//1. 弹出提示框
this.$confirm("些操作永久删除当前信息,是否继续?", "提示", {type: "info"}).then(() => {
//2. 做删除业务
axios.delete("/books/" + row.id).then((res) => {
//判断当前操作是否成功
if (res.data.flag) {
this.$message.success("删除成功");
} else {
this.$message.error("数据同步失败,自动刷新");
}
}).finally(() => {
//2.重新加载数据
this.getAll();
});
}).catch(() => {
//3. 取消删除
this.$message.info("取消操作");
});
},
小结:
- 加载要修改数据通过传递当前行数据对应的 id 值到后台查询数据
- 利用前端数据双向绑定将查询到的数据进行回显
# 45 - 修改功能
- 修改
//修改
handleEdit() {
axios.put("/books", this.formData).then((res) => {
//判断当前操作是否成功
if (res.data.flag) {
//1.关闭弹层
this.dialogFormVisible4Edit = false;
this.$message.success("修改成功");
} else {
this.$message.error("修改失败");
}
}).finally(() => {
//2.重新加载数据
this.getAll();
});
},
- 取消添加和修改
//取消
cancel() {
//1.关闭弹层
this.dialogFormVisible = false;
this.dialogFormVisible4Edit = false;
//2.提示用户
this.$message.info("当前操作取消");
},
小结:
- 请求方式使用 PUT 调用后台对应操作
- 修改操作结束后动态刷新页面加载数据(同新增)
- 根据操作结果不同,显示对应的提示信息(同新增)
# 46 - 异常消息处理
- 业务操作成功或失败返回数据格式
{
"flag": true,
"data": null
}
{
"flag": false,
"data": null
}
- 后台代码 BUG 导致数据格式不统一性
{
"timestamp": "2021-11-07T12:44:29.343+00:00",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"path": "/books"
}
- 对异常进行统一处理,出现异常后,返回指定信息
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ProjectExceptionAdvice {
//拦截所有的异常信息
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public R doException(Exception ex) {
// 记录日志
// 发送消息给运维
// 发送邮件给开发人员 ,ex 对象发送给开发人员
ex.printStackTrace();
return new R(false, null, "系统错误,请稍后再试!");
}
}
- 修改表现层返回结果的模型类,封装出现异常后对应的信息
flag:false
Data: null
消息 (msg): 要显示信息
@Data
public class R{
private Boolean flag;
private Object data;
private String msg;
public R(Boolean flag,Object data,String msg){
this.flag = flag;
this.data = data;
this.msg = msg;
}
}
- 页面消息处理,没有传递消息加载默认消息,传递消息后加载指定消息
//添加
handleAdd() {
axios.post("/books", this.formData).then((res) => {
//判断当前操作是否成功
if (res.data.flag) {
//1.关闭弹层
this.dialogFormVisible = false;
this.$message.success("添加成功");
} else {
this.$message.error(res.data.msg);
}
}).finally(() => {
//2.重新加载数据
this.getAll();
})
},
- 可以在表现层 Controller 中进行消息统一处理
@PostMapping
public R save(@RequestBody Book book) throws IOException {
//if (book.getName().equals("123")) throw new IOException();
boolean flag = bookService.save(book);
return new R(flag, flag ? "添加成功^_^" : "添加失败-_-!");
}
- 页面消息处理
//添加
handleAdd() {
axios.post("/books", this.formData).then((res) => {
//判断当前操作是否成功
if (res.data.flag) {
//1.关闭弹层
this.dialogFormVisible = false;
this.$message.success(res.data.msg);
} else {
this.$message.error(res.data.msg);
}
}).finally(() => {
//2.重新加载数据
this.getAll();
})
},
小结:
- 使用注解 @RestControllerAdvice 定义 SpringMVC 异常处理器用来处理异常的
- 异常处理器必须被扫描加载,否则无法生效
- 表现层返回结果的模型类中添加消息属性用来传递消息到页面
# 47 - 分页
- 页面使用 el 分页组件添加分页功能
<!--分页组件-->
<div class="pagination-container">
<el-pagination
class="pagiantion"
@current-change="handleCurrentChange"
:current-page="pagination.currentPage"
:page-size="pagination.pageSize"
layout="total, prev, pager, next, jumper"
:total="pagination.total">
</el-pagination>
</div>
- 定义分页组件需要使用的数据并将数据绑定到分页组件
data: {
pagination: { // 分页相关模型数据
currentPage: 1, // 当前页码
pageSize: 10, // 每页显示的记录数
total: 0, // 总记录数
}
},
- 替换查询全部功能为分页功能
getAll() {
axios.get("/books/" + this.pagination.currentPage + "/" + this.pagination.pageSize).then((res) => {});
},
- 分页查询
使用路径参数传递分页数据或封装对象传递数据
@GetMapping("{currentPage}/{pageSize}")
public R getPage(@PathVariable Integer currentPage, @PathVariable int pageSize) {
return new R(true, bookService.getPage(currentPage, pageSize));
}
- 加载分页数据
//分页查询
getAll() {
//发送异步请求
axios.get("/books/" + this.pagination.currentPage + "/" + this.pagination.pageSize).then((res) => {
//console.log(res.data);
this.pagination.currentPage = res.data.data.current;
this.pagination.pageSize = res.data.data.size;
this.pagination.total = res.data.data.total;
this.dataList = res.data.data.records;
})
},
- 分页页码值切换
//切换页码
handleCurrentChange(currentPage) {
//修改页码值为当前选中的页码值
this.pagination.currentPage = currentPage;
//执行查询
this.getAll();
},
小结:
- 使用 el 分页组件
- 定义分页组件绑定的数据模型
- 异步调用获取分页数据
- 分页数据页面回显
# 48 - 分页功能维护(删除 BUG)
- 对查询结果进行校验,如果当前页码值大于最大页码值,使用最大页码值作为当前页码值重新查询
@GetMapping("{currentPage}/{pageSize}")
public R getPage(@PathVariable Integer currentPage, @PathVariable int pageSize) {
IPage<Book> page = bookService.getPage(currentPage, pageSize);
// 如果当前页码值大于了总页码值,那么重新执行查询操作,使用最大页码值作为当前页码值
if (currentPage > page.getPages()) {
page = bookService.getPage((int) page.getPages(), pageSize);
}
return new R(true, page);
}
小结:
- 基于业务需求维护删除功能
# 49 - 条件查询
- 查询条件数据封装
单独封装
与分页操作混合封装
pagination: {//分页相关模型数据
currentPage: 1,//当前页码
pageSize: 10,//每页显示的记录数
total: 0,//总记录数
type: "",
name: "",
description: ""
}
- 页面数据模型绑定
<div class="filter-container">
<el-input placeholder="图书类别" v-model="pagination.type" class="filter-item" />
<el-input placeholder="图书名称" v-model="pagination.name" class="filter-item" />
<el-input placeholder="图书描述" v-model="pagination.description" class="filter-item" />
<el-button @click="getAll()" class="dalfBut">查询</el-button>
<el-button type="primary" class="butT" @click="handleCreate()">新建</el-button>
</div>
- 组织数据成为 get 请求发送的数据
//分页查询
getAll() {
console.log(this.pagination.type);
// /books/1/10?type=???&name=???&decription=?? ;
//1. 获取查询条件 , 拼接查询条件
param = "?name=" + this.pagination.name;
param += "&type=" + this.pagination.type;
param += "&description=" + this.pagination.description;
//console.log("-----------------" + param);
//发送异步请求
axios.get("/books/" + this.pagination.currentPage + "/" + this.pagination.pageSize + param).then((res) => {
//console.log(res.data);
this.pagination.currentPage = res.data.data.current;
this.pagination.pageSize = res.data.data.size;
this.pagination.total = res.data.data.total;
this.dataList = res.data.data.records;
})
},
- 条件参数组织可以通过条件判定书写的更简洁
- Controller 接收参数
@GetMapping("{currentPage}/{pageSize}")
public R getAll(@PathVariable int currentPage,@PathVariable int pageSize,Book book) {
System.out.println("参数=====>"+book);
IPage<Book> pageBook = bookService.getPage(currentPage,pageSize);
return new R(null != pageBook ,pageBook);
}
- 业务层接口功能开发
/**
* 分页的条件查询
*
* @param currentPage
* @param pageSize
* @param book
* @return
*/
IPage<Book> getPage(Integer currentPage, int pageSize, Book book);
- 业务层接口实现类功能开发
@Override
public IPage<Book> getPage(Integer currentPage, int pageSize, Book book) {
LambdaQueryWrapper<Book> lambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
lambdaQueryWrapper.like(Strings.isNotEmpty(book.getType()), Book::getType, book.getType());
lambdaQueryWrapper.like(Strings.isNotEmpty(book.getName()), Book::getName, book.getName());
lambdaQueryWrapper.like(Strings.isNotEmpty(book.getDescription()), Book::getDescription, book.getDescription());
IPage page = new Page(currentPage, pageSize);
bookDao.selectPage(page, lambdaQueryWrapper);
return page;
}
- Controller 调用业务层分页条件查询接口
@GetMapping("{currentPage}/{pageSize}")
public R getPage(@PathVariable Integer currentPage, @PathVariable int pageSize, Book book) {
// System.out.println("book=>" + book);
IPage<Book> page = bookService.getPage(currentPage, pageSize, book);
// 如果当前页码值大于了总页码值,那么重新执行查询操作,使用最大页码值作为当前页码值
if (currentPage > page.getPages()) {
page = bookService.getPage((int) page.getPages(), pageSize, book);
}
return new R(true, page);
}
- 页面回显数据
//分页查询
getAll() {
console.log(this.pagination.type);
// /books/1/10?type=???&name=???&decription=?? ;
//1. 获取查询条件 , 拼接查询条件
param = "?name=" + this.pagination.name;
param += "&type=" + this.pagination.type;
param += "&description=" + this.pagination.description;
//console.log("-----------------" + param);
//发送异步请求
axios.get("/books/" + this.pagination.currentPage + "/" + this.pagination.pageSize + param).then((res) => {
//console.log(res.data);
this.pagination.currentPage = res.data.data.current;
this.pagination.pageSize = res.data.data.size;
this.pagination.total = res.data.data.total;
this.dataList = res.data.data.records;
})
},
小结:
- 定义查询条件数据模型(当前封装到分页数据模型中)
- 异步调用分页功能并通过请求参数传递数据到后台
# 50 - 基础篇完结
# 基于 SpringBoot 的 SSMP 整合案例
- pom.xml
配置起步依赖 - application.yml
设置数据源、端口、框架技术相关配置等 - dao
继承 BaseMapper、设置 @Mapper - dao 测试类
- service
调用数据层接口或 MyBatis-Plus 提供的接口快速开发 - service 测试类
- controller
基于 Restful 开发,使用 Postman 测试跑通功能 - 页面
放置在 resources 目录下的 static 目录中
总结:
- 整合 JUint
- 整合 MyBatis
- 整合 MyBatis-Plus
- 整合 Druid
- 基于 SpringBoot 的 SSMP 整合案例
# 后续学习
- 基础篇
- 能够创建 SpringBoot 工程
- 基于 SpringBoot 实现 ssm/ssmp 整合
- 实用篇
- 运维实用篇 Spring Boot 2 运维实用篇学习笔记
- 能够掌握 SpringBoot 程序多环境开发
- 能够基于 Linux 系统发布 SpringBoot 工程
- 能够解决线上灵活配置 SpringBoot 工程的需求
- 开发实用篇
- 能够基于 SpringBoot 整合任意第三方技术
- 运维实用篇 Spring Boot 2 运维实用篇学习笔记
- 原理篇